Heat transfer from extended surfaces fins pdf
24/03/2017 · 27 videos Play all Heat Transfer: Dr. John Biddle’s Lecture Series CPPMechEngTutorials Thermodynamics and the End of the Universe: Energy, Entropy, and the fundamental laws of physics. – Duration
Advances and Outlooks of Heat Transfer Enhancement by Longitudinal Vortex Generators such as treated surfaces, rough surfaces, extended surfaces, swirl flow devices, and additives to the fluid, do not require any external powers. On the other hand, the active techniques, such as vibration, electromagnetic field and jet impingement, require external power to enhance heat transfer. In order
In this study heat transfer performances of extended surfaces (fins) having square, circular, hexagonal, and triangular lateral perforations are studied numerically.
View heattransferfromextendedsurfacesorfins-160904100723.pdf from MECH ME 555 at Southern New Hampshire University. Lectures on Heat Transfer -HEAT TRANSFER FROM
Title: : Heat Transfer Phenomenon of Extended Surfaces in Form of Fins with Internal and External Configurations: A Review PaperId: : 9146 Published in: Internation Journal Of Advance Research And Innovative Ideas In Education
2 3/83 Techniques of Heat Transfer Enhan cement and their Application 1. Introduction This chapter discusses enhanced extended surface geometries for the plate-and-fin heat exchanger
The heat transfer characteristics of fins are known as conduction-convection systems. Consider a cylindrical fin with a heat source located at its base and its surface is exposed to a surrounding.
Extended Surface Heat Transfer . 3.1 Introduction: Convection: Heat transfer between a solid surface and a moving fluid is governed by the effective surface area by using fins or extended surfaces. Fins are protrusions from the base surface into the cooling fluid, so that the extra surface of the protrusions is also in contact with the fluid. Most of you have encountered cooling fins on
Fins in heat and mass transfer for College students
Abstract – The main purpose of extended surfaces called fins to increase the heat transfer rate. Many types of fins investigated and different result comes. Both experimentally work or numerically work done by researcher to conclude the results with different types of fins such as rectangular, v-type, notched, unnotched fins with different medium such as water and air to increase the heat
Extended Surfaces (Fins) are widely used in the engineering for getting better heat transfer by providing additional area. In many applications like heat exchangers, for cooling reactor core, electrical transformer, rectifier, etc fins are used for better heat transfer. This work is carried out for find out which material and which cross sectional fin is best suited for the better heat
EXTENDED SURFACES / FINS Convection: Heat transfer between a solid surface and a moving fluid is governed by the Newton’s cooling law: q = hA(T s -T ). Therefore, to increase the convective heat transfer, one can Increase the temperature difference (T. s -T ) between the surface and the fluid. Increase the convection coefficient h. This can be accomplished by increasing the fluid flow over
Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces. 1. General Considerations – Extended Surface refers to a solid material in which energy is transferred by conduction within its boundaries and by
where T(x) is the temperature of the fin at a particular dimensional position x (refer “Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces” section in [1]). In order to simplify the expression, non-dimensionalize by introducing the following definitions:
A fin is a surface that extends from an object to increase the rate of heat transfer to or from the environment by increasing convection. Extensions on the finned surfaces is used to increases the surface area of the fin in contact with
EXTENDED SURFACES / FINS Convection: Heat transfer between a solid surface and a moving fluid is governed by the Newton’s cooling law: q = hA(T
extended surfaces such as boundary conditions and analysis. Arora et al.[2] in functions in the analysis of extended surface heat transfer and differential equations are formulated from the fundamentals of conduction and convection heat transfer. Rahim et al. [7] in their paper analysed heat transfer through a wall containing triangular fins partially embedded in its volume, Coupled heat
Fins as extended surfaces have wide applications in heat transfer augmentation techniques. The solutions are already available in analytical form. This OCTAVE script tries to prepare a plug-and-calculate method for straight fins for all possible combinations of boundary conditions.
extended surfaces Thermal Conduction Heat Transfer

Heat Transfer Phenomenon of Extended Surfaces in Form of
been discussed and heat transfer through extended surfaces or fins and various methods of increasing heat transfer are discussed. Extended Surface (Fin) are used to enhance convective heat transfer in a wide range of engineering applications and offer a practical means for achieving a large total heat transfer surface area without the use of an excessive amount of primary surface area. Fins
Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET)
A fin is a surface that extends from an object to increase the rate of heat transfer to or from the environment by increasing convection heat transfer, The term (extended surface) is commonly used
– If heat is transferred from the surface to the fluid by convection.Nature and Rationale Nature and Rationale of Extended Surfaces • An extended surface (also know as a combined conduction-convection system or a fin) is a solid within which heat transfer …
Extended surfaces are extensively used in air-cooled automobile engines, air-conditioning systems, oil industries, computer processors, and other electronic devices. In various applications heat from the fins …
No. 2744 Efficiency of Extended Surfaces with Simultaneous Heat and Mass Transfer A.H. Elmahdy R.C. Biggs ASHRA E Member ABSTRACT An algorithm is presented to determine the efficiency of extended surfaces (circular or
Extended surfaces (fins) are one of the heat exchanging devices that are employed extensively to increase heat transfer rates. The rate of heat transfer depends on the surfacearea of the fin
The present article investigates the effect of locally variable heat transfer coefficient on the performance of extended surfaces (fins) subject to natural convection. Fins of different profiles have been investigated. The fin profiles presently considered are namely; straight and pin fin with
Keywords Fins, Heat exchanger, Surfaces Abstract A three-dimensional numerical study was conducted to assess the heat transfer perfor- mance of extended fins in a two-row finned tube heat exchanger.
EXTENDED SURFACES FIN PERFORMANCE FIN EFFICIENCY .Fin Efficiency may be defined as the ratio of actual heat lost by the fin to the maximum heat lost by the fin. The maximum rate at which a fin could dissipate energy, is the rate that would exist, if the entire fin surface were at the base temperature lact Qmax ninc erefore, Qact fin Qmax A. Infinitely Long Fin ml
these cases, certain type of heat exchange surfaces, called extended surfaces, have been developed in which outside area of tube is increased many fold by fins and other appendages. Two types of fins, are in common use viz; longitudinal fins and transverse fins.
analysis of the heat transfer growth and the respective pressure drop below a flat surface embedded with ring shaped or circular square perforated fins in a rectangular manner.
– radiation heat transfer from and to the fin is neglected In general, the study of the extended surface heat transfer compromises the movement of the heat within the fin by conduction and the process of the heat exchange between the fin
Use of extended surface or fin to enhance heat transfer. Look on the plane side-view of the surface and the surface with fin. The heat transfer rate without the fin from area A to the surrounding fluid is
The heat flow from a primary surface with fins attached is a combination of the flow from the area of the surface not covered by the fins and the flow through the fins. Therefore knowledge of the temperature distribution through both the primary surface and the attached fins is necessary in order to design the extended surface assembly.
INTRODUCTION Faculty Server Contact
24/03/2017 · 27 videos Play all Heat Transfer: Dr. John Biddle’s Lecture Series CPPMechEngTutorials Thermodynamics and the End of the Universe: Energy, Entropy, and the fundamental laws of physics. – …
What is a Fin? • A fin is a extended surface to increase area for convection heat transfer • Goal is to increase A s to increase • Automobile radiator is example of fin Figure 3-33 from Çengel, Heat Transfer Q&=hAs()Ts −T∞ Q& 10 Innovative Fin Designs Figure 3-34 from Çengel, Heat Transfer • Important application is cooling of power electronics • How do we analyze fin
Updated 10/8/2015. Extended Surfaces (Fins) The normal textbook treatment of heat transfer from fins involves the solution by analytical means of an ordinary differential equation describing transport by conduction along the fin and convection from its surface.
Heat transfer inside fin systems composed of primary rectangular fins with large number of slender rods attached on their surfaces is modeled and analyzed analytically in this work. The
Heat Transfer from Extended Surface (Fin) A fin is a surface that extends from an object to increase the rate of heat transfer to or from the environment by increase convection. Adding a fin to an object increases the surface area and can sometimes be an economical solution to heat transfer problems. – cfa code of ethics handbook In the study of heat transfer, fins are surfaces that extend from an object to increase the rate of heat transfer to or from the environment by increasing convection.
The surface area exposed to the surroundings is frequently increased by the attachment of protrusions to the surfaces, and the arrangement provides a means by which heat transfer rate can be substantially improved. The protrusions are called fins or spines, and these extensions can take a variety of forms.
Common Assumptions for Fins •Finned surfaces are commonly used in practice to enhance heat transfer •In the analysis of fins, we consider steady
extended surfaces / fins Convection: Heat transfer between a solid surface and a moving fluid is governed by the Newton’s cooling law: q = hA(Ts-T∞). Therefore, to increase the convective heat transfer, one can Increase the temperature difference (Ts-T∞) between the surface and the fluid.
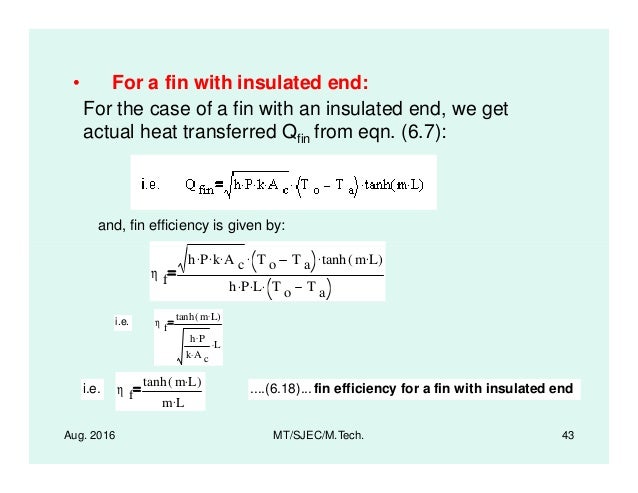
Heat and Mass Transfer Heat Transfer Formula Sheet and Tables Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces (Fins) Case I: very long fin Case II: fin with a finite length, L, and the end is insulated Case III: fin with a finite length, L, and losses heat by convection from its end Fin Efficiency: Convection
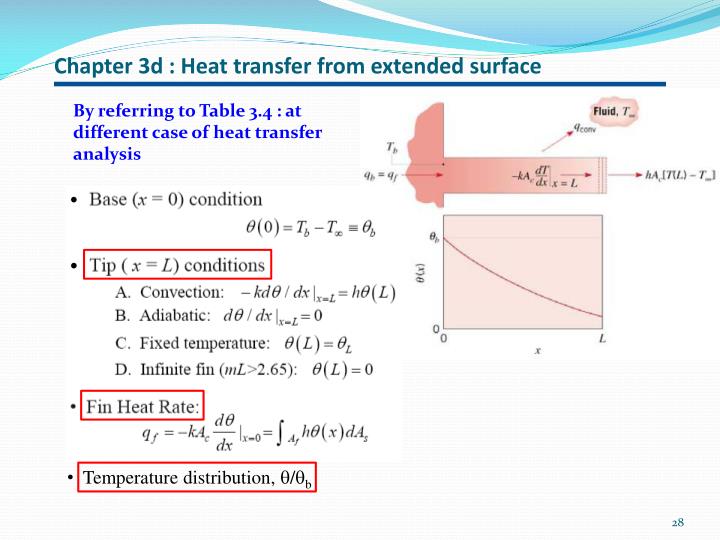
Heat Transfer for Fins (or Extended Surfaces) Handout Table 3.4 Fin temperature distribution, € θ=T−T ∞, and heat loss, q f, for uniform cross section
Extended Surfaces/Fins Convection: Heat transfer between a solid surface and a moving fluid is governed by the Newton’s cooling law: q = hA(T
15/01/2016 · This lecture covers the following topics: 1. Important parameters which affect the heat transfer from surfaces 2. Governing equation for temperature distribution in a fin 3. Infinitely long fin …
Enhancement of Heat Exchanger Performance by the Extended
transfer surfaces and also the consideration of various performance constraints and parameters of fins (extended surfaces). The primary task of fins employed in highly effective heat exchanger is to increase the heat transfer
Fins are used to enhance heat transfer, and the use of fins on a surface cannot be recommended unless the enhancement in heat transfer justifies the added cost and complexity associated with the fins.
This paper attempts to provide a comprehensive, coherent, and methodical review of the existing literature on the transient performance of extended surfaces (fins).
This file contains slides on Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces (FINS). The slides were prepared while teaching Heat Transfer course to the M.Tech. students … The slides were prepared while teaching Heat Transfer course to the M.Tech. students …
Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces Part 2 CH EN 3453 – Heat Transfer Reminders… • Homework #3 due today • Homework #4 due Friday next week
In case of extended surfaces, effective heat transfer area on the side of the extended surface is increased. Passive techniques hold the advantage over the active techniques as they do not require any direct input of external power. These techniques do not require any direct input of external power; rather they use it from the system itself which ultimately leads to an increase in fluid
Extended Surfaces (Fins) University of Virginia
Extended surface heat transfer—the dovetail fin
Extended surface heat transfer—the Dovetail Fin Request PDF
Heat transfer from extended surfaces (or fins) SlideShare
Fins and Extended Surfaces Heat Transfer Applications
Heat and Mass Transfer Heat Transfer Formula Sheet and
Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces Part 2
– Experimental Study of Extended Surfaces (Fins) With Forced
Transient Heat Transfer in Extended Surfaces Applied
heattransferfromextendedsurfacesorfins-160904100723.pdf
Lecture 11 Hear Transfer from Extended Surfaces (Fins
Heat Transfer Enhancement from Heat Sinks using Perforated
Review of utilization of extended surfaces in heat
analysis of the heat transfer growth and the respective pressure drop below a flat surface embedded with ring shaped or circular square perforated fins in a rectangular manner.
24/03/2017 · 27 videos Play all Heat Transfer: Dr. John Biddle’s Lecture Series CPPMechEngTutorials Thermodynamics and the End of the Universe: Energy, Entropy, and the fundamental laws of physics. – …
In the study of heat transfer, fins are surfaces that extend from an object to increase the rate of heat transfer to or from the environment by increasing convection.
these cases, certain type of heat exchange surfaces, called extended surfaces, have been developed in which outside area of tube is increased many fold by fins and other appendages. Two types of fins, are in common use viz; longitudinal fins and transverse fins.
Heat Transfer for Fins (or Extended Surfaces) Handout Table 3.4 Fin temperature distribution, € θ=T−T ∞, and heat loss, q f, for uniform cross section
This file contains slides on Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces (FINS). The slides were prepared while teaching Heat Transfer course to the M.Tech. students … The slides were prepared while teaching Heat Transfer course to the M.Tech. students …
A fin is a surface that extends from an object to increase the rate of heat transfer to or from the environment by increasing convection heat transfer, The term (extended surface) is commonly used
The heat flow from a primary surface with fins attached is a combination of the flow from the area of the surface not covered by the fins and the flow through the fins. Therefore knowledge of the temperature distribution through both the primary surface and the attached fins is necessary in order to design the extended surface assembly.
Temperature Distribution along a Constant Cross Sectional
Extended Surfaces / Fins Heat Transfer Convection
This file contains slides on Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces (FINS). The slides were prepared while teaching Heat Transfer course to the M.Tech. students … The slides were prepared while teaching Heat Transfer course to the M.Tech. students …
No. 2744 Efficiency of Extended Surfaces with Simultaneous Heat and Mass Transfer A.H. Elmahdy R.C. Biggs ASHRA E Member ABSTRACT An algorithm is presented to determine the efficiency of extended surfaces (circular or
In the study of heat transfer, fins are surfaces that extend from an object to increase the rate of heat transfer to or from the environment by increasing convection.
A fin is a surface that extends from an object to increase the rate of heat transfer to or from the environment by increasing convection heat transfer, The term (extended surface) is commonly used
The heat transfer characteristics of fins are known as conduction-convection systems. Consider a cylindrical fin with a heat source located at its base and its surface is exposed to a surrounding.
In case of extended surfaces, effective heat transfer area on the side of the extended surface is increased. Passive techniques hold the advantage over the active techniques as they do not require any direct input of external power. These techniques do not require any direct input of external power; rather they use it from the system itself which ultimately leads to an increase in fluid
Common Assumptions for Fins •Finned surfaces are commonly used in practice to enhance heat transfer •In the analysis of fins, we consider steady
Extended surfaces (fins) are one of the heat exchanging devices that are employed extensively to increase heat transfer rates. The rate of heat transfer depends on the surfacearea of the fin
What is a Fin? • A fin is a extended surface to increase area for convection heat transfer • Goal is to increase A s to increase • Automobile radiator is example of fin Figure 3-33 from Çengel, Heat Transfer Q&=hAs()Ts −T∞ Q& 10 Innovative Fin Designs Figure 3-34 from Çengel, Heat Transfer • Important application is cooling of power electronics • How do we analyze fin
Heat transfer inside fin systems composed of primary rectangular fins with large number of slender rods attached on their surfaces is modeled and analyzed analytically in this work. The
CFDyna.com Heat Transfer in Extended Surfaces Fins
Effects of Perforation Geometry on the Heat Transfer
Title: : Heat Transfer Phenomenon of Extended Surfaces in Form of Fins with Internal and External Configurations: A Review PaperId: : 9146 Published in: Internation Journal Of Advance Research And Innovative Ideas In Education
24/03/2017 · 27 videos Play all Heat Transfer: Dr. John Biddle’s Lecture Series CPPMechEngTutorials Thermodynamics and the End of the Universe: Energy, Entropy, and the fundamental laws of physics. – Duration
A fin is a surface that extends from an object to increase the rate of heat transfer to or from the environment by increasing convection heat transfer, The term (extended surface) is commonly used
In case of extended surfaces, effective heat transfer area on the side of the extended surface is increased. Passive techniques hold the advantage over the active techniques as they do not require any direct input of external power. These techniques do not require any direct input of external power; rather they use it from the system itself which ultimately leads to an increase in fluid
Enhancement of Heat Exchanger Performance by the Extended
Heat Transfer in Extended Surfaces (FINS) Fundamentals
Advances and Outlooks of Heat Transfer Enhancement by Longitudinal Vortex Generators such as treated surfaces, rough surfaces, extended surfaces, swirl flow devices, and additives to the fluid, do not require any external powers. On the other hand, the active techniques, such as vibration, electromagnetic field and jet impingement, require external power to enhance heat transfer. In order
Fins are used to enhance heat transfer, and the use of fins on a surface cannot be recommended unless the enhancement in heat transfer justifies the added cost and complexity associated with the fins.
In this study heat transfer performances of extended surfaces (fins) having square, circular, hexagonal, and triangular lateral perforations are studied numerically.
EXTENDED SURFACES / FINS Convection: Heat transfer between a solid surface and a moving fluid is governed by the Newton’s cooling law: q = hA(T s -T ). Therefore, to increase the convective heat transfer, one can Increase the temperature difference (T. s -T ) between the surface and the fluid. Increase the convection coefficient h. This can be accomplished by increasing the fluid flow over
This paper attempts to provide a comprehensive, coherent, and methodical review of the existing literature on the transient performance of extended surfaces (fins).
Extended surfaces (fins) are one of the heat exchanging devices that are employed extensively to increase heat transfer rates. The rate of heat transfer depends on the surfacearea of the fin
– If heat is transferred from the surface to the fluid by convection.Nature and Rationale Nature and Rationale of Extended Surfaces • An extended surface (also know as a combined conduction-convection system or a fin) is a solid within which heat transfer …
ONE DIMENSIONAL TRIANGULAR FIN EXPERIMENT
Heat Transfer in Extended Surfaces (FINS) Fundamentals
Advances and Outlooks of Heat Transfer Enhancement by Longitudinal Vortex Generators such as treated surfaces, rough surfaces, extended surfaces, swirl flow devices, and additives to the fluid, do not require any external powers. On the other hand, the active techniques, such as vibration, electromagnetic field and jet impingement, require external power to enhance heat transfer. In order
extended surfaces such as boundary conditions and analysis. Arora et al.[2] in functions in the analysis of extended surface heat transfer and differential equations are formulated from the fundamentals of conduction and convection heat transfer. Rahim et al. [7] in their paper analysed heat transfer through a wall containing triangular fins partially embedded in its volume, Coupled heat
15/01/2016 · This lecture covers the following topics: 1. Important parameters which affect the heat transfer from surfaces 2. Governing equation for temperature distribution in a fin 3. Infinitely long fin …
EXTENDED SURFACES FIN PERFORMANCE FIN EFFICIENCY .Fin Efficiency may be defined as the ratio of actual heat lost by the fin to the maximum heat lost by the fin. The maximum rate at which a fin could dissipate energy, is the rate that would exist, if the entire fin surface were at the base temperature lact Qmax ninc erefore, Qact fin Qmax A. Infinitely Long Fin ml
Extended Surfaces (Fins) are widely used in the engineering for getting better heat transfer by providing additional area. In many applications like heat exchangers, for cooling reactor core, electrical transformer, rectifier, etc fins are used for better heat transfer. This work is carried out for find out which material and which cross sectional fin is best suited for the better heat
EXTENDED SURFACES / FINS Convection: Heat transfer between a solid surface and a moving fluid is governed by the Newton’s cooling law: q = hA(T
– radiation heat transfer from and to the fin is neglected In general, the study of the extended surface heat transfer compromises the movement of the heat within the fin by conduction and the process of the heat exchange between the fin
Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces Part 2 CH EN 3453 – Heat Transfer Reminders… • Homework #3 due today • Homework #4 due Friday next week
Extended surfaces (fins) are one of the heat exchanging devices that are employed extensively to increase heat transfer rates. The rate of heat transfer depends on the surfacearea of the fin
Extended Surfaces / Fins Heat Transfer Convection
Efficiency of extended surfaces with simultaneous heat and
been discussed and heat transfer through extended surfaces or fins and various methods of increasing heat transfer are discussed. Extended Surface (Fin) are used to enhance convective heat transfer in a wide range of engineering applications and offer a practical means for achieving a large total heat transfer surface area without the use of an excessive amount of primary surface area. Fins
In the study of heat transfer, fins are surfaces that extend from an object to increase the rate of heat transfer to or from the environment by increasing convection.
EXTENDED SURFACES / FINS Convection: Heat transfer between a solid surface and a moving fluid is governed by the Newton’s cooling law: q = hA(T s -T ). Therefore, to increase the convective heat transfer, one can Increase the temperature difference (T. s -T ) between the surface and the fluid. Increase the convection coefficient h. This can be accomplished by increasing the fluid flow over
A fin is a surface that extends from an object to increase the rate of heat transfer to or from the environment by increasing convection heat transfer, The term (extended surface) is commonly used
analysis of the heat transfer growth and the respective pressure drop below a flat surface embedded with ring shaped or circular square perforated fins in a rectangular manner.
Extended Surfaces (Fins) are widely used in the engineering for getting better heat transfer by providing additional area. In many applications like heat exchangers, for cooling reactor core, electrical transformer, rectifier, etc fins are used for better heat transfer. This work is carried out for find out which material and which cross sectional fin is best suited for the better heat
Abstract – The main purpose of extended surfaces called fins to increase the heat transfer rate. Many types of fins investigated and different result comes. Both experimentally work or numerically work done by researcher to conclude the results with different types of fins such as rectangular, v-type, notched, unnotched fins with different medium such as water and air to increase the heat
2 3/83 Techniques of Heat Transfer Enhan cement and their Application 1. Introduction This chapter discusses enhanced extended surface geometries for the plate-and-fin heat exchanger
Fins are used to enhance heat transfer, and the use of fins on a surface cannot be recommended unless the enhancement in heat transfer justifies the added cost and complexity associated with the fins.
Extended surfaces are extensively used in air-cooled automobile engines, air-conditioning systems, oil industries, computer processors, and other electronic devices. In various applications heat from the fins …
Fins as extended surfaces have wide applications in heat transfer augmentation techniques. The solutions are already available in analytical form. This OCTAVE script tries to prepare a plug-and-calculate method for straight fins for all possible combinations of boundary conditions.
No. 2744 Efficiency of Extended Surfaces with Simultaneous Heat and Mass Transfer A.H. Elmahdy R.C. Biggs ASHRA E Member ABSTRACT An algorithm is presented to determine the efficiency of extended surfaces (circular or
A fin is a surface that extends from an object to increase the rate of heat transfer to or from the environment by increasing convection. Extensions on the finned surfaces is used to increases the surface area of the fin in contact with
Extended surfaces (fins) are one of the heat exchanging devices that are employed extensively to increase heat transfer rates. The rate of heat transfer depends on the surfacearea of the fin
Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET)
BASCO TYPE ES EXTENDED SURFACE PLATE FIN HEAT
Extended Surfaces/Fins mycsvtunotes.weebly.com
Fins as extended surfaces have wide applications in heat transfer augmentation techniques. The solutions are already available in analytical form. This OCTAVE script tries to prepare a plug-and-calculate method for straight fins for all possible combinations of boundary conditions.
transfer surfaces and also the consideration of various performance constraints and parameters of fins (extended surfaces). The primary task of fins employed in highly effective heat exchanger is to increase the heat transfer
Extended surfaces (fins) are one of the heat exchanging devices that are employed extensively to increase heat transfer rates. The rate of heat transfer depends on the surfacearea of the fin
The heat flow from a primary surface with fins attached is a combination of the flow from the area of the surface not covered by the fins and the flow through the fins. Therefore knowledge of the temperature distribution through both the primary surface and the attached fins is necessary in order to design the extended surface assembly.
Fins are used to enhance heat transfer, and the use of fins on a surface cannot be recommended unless the enhancement in heat transfer justifies the added cost and complexity associated with the fins.
Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces Part 2 CH EN 3453 – Heat Transfer Reminders… • Homework #3 due today • Homework #4 due Friday next week
– radiation heat transfer from and to the fin is neglected In general, the study of the extended surface heat transfer compromises the movement of the heat within the fin by conduction and the process of the heat exchange between the fin
The heat transfer characteristics of fins are known as conduction-convection systems. Consider a cylindrical fin with a heat source located at its base and its surface is exposed to a surrounding.
This paper attempts to provide a comprehensive, coherent, and methodical review of the existing literature on the transient performance of extended surfaces (fins).
View heattransferfromextendedsurfacesorfins-160904100723.pdf from MECH ME 555 at Southern New Hampshire University. Lectures on Heat Transfer -HEAT TRANSFER FROM
Heat Transfer from Extended Surface (Fin) A fin is a surface that extends from an object to increase the rate of heat transfer to or from the environment by increase convection. Adding a fin to an object increases the surface area and can sometimes be an economical solution to heat transfer problems.
Keywords Fins, Heat exchanger, Surfaces Abstract A three-dimensional numerical study was conducted to assess the heat transfer perfor- mance of extended fins in a two-row finned tube heat exchanger.
where T(x) is the temperature of the fin at a particular dimensional position x (refer “Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces” section in [1]). In order to simplify the expression, non-dimensionalize by introducing the following definitions:
analysis of the heat transfer growth and the respective pressure drop below a flat surface embedded with ring shaped or circular square perforated fins in a rectangular manner.
been discussed and heat transfer through extended surfaces or fins and various methods of increasing heat transfer are discussed. Extended Surface (Fin) are used to enhance convective heat transfer in a wide range of engineering applications and offer a practical means for achieving a large total heat transfer surface area without the use of an excessive amount of primary surface area. Fins
INTRODUCTION Faculty Server Contact
Review of utilization of extended surfaces in heat
In case of extended surfaces, effective heat transfer area on the side of the extended surface is increased. Passive techniques hold the advantage over the active techniques as they do not require any direct input of external power. These techniques do not require any direct input of external power; rather they use it from the system itself which ultimately leads to an increase in fluid
Advances and Outlooks of Heat Transfer Enhancement by Longitudinal Vortex Generators such as treated surfaces, rough surfaces, extended surfaces, swirl flow devices, and additives to the fluid, do not require any external powers. On the other hand, the active techniques, such as vibration, electromagnetic field and jet impingement, require external power to enhance heat transfer. In order
Updated 10/8/2015. Extended Surfaces (Fins) The normal textbook treatment of heat transfer from fins involves the solution by analytical means of an ordinary differential equation describing transport by conduction along the fin and convection from its surface.
Common Assumptions for Fins •Finned surfaces are commonly used in practice to enhance heat transfer •In the analysis of fins, we consider steady
This paper attempts to provide a comprehensive, coherent, and methodical review of the existing literature on the transient performance of extended surfaces (fins).
View heattransferfromextendedsurfacesorfins-160904100723.pdf from MECH ME 555 at Southern New Hampshire University. Lectures on Heat Transfer -HEAT TRANSFER FROM
The surface area exposed to the surroundings is frequently increased by the attachment of protrusions to the surfaces, and the arrangement provides a means by which heat transfer rate can be substantially improved. The protrusions are called fins or spines, and these extensions can take a variety of forms.
This file contains slides on Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces (FINS). The slides were prepared while teaching Heat Transfer course to the M.Tech. students … The slides were prepared while teaching Heat Transfer course to the M.Tech. students …
Heat Transfer from Extended Surface (Fin) A fin is a surface that extends from an object to increase the rate of heat transfer to or from the environment by increase convection. Adding a fin to an object increases the surface area and can sometimes be an economical solution to heat transfer problems.
– If heat is transferred from the surface to the fluid by convection.Nature and Rationale Nature and Rationale of Extended Surfaces • An extended surface (also know as a combined conduction-convection system or a fin) is a solid within which heat transfer …
What is a Fin? • A fin is a extended surface to increase area for convection heat transfer • Goal is to increase A s to increase • Automobile radiator is example of fin Figure 3-33 from Çengel, Heat Transfer Q&=hAs()Ts −T∞ Q& 10 Innovative Fin Designs Figure 3-34 from Çengel, Heat Transfer • Important application is cooling of power electronics • How do we analyze fin
Extended surfaces are extensively used in air-cooled automobile engines, air-conditioning systems, oil industries, computer processors, and other electronic devices. In various applications heat from the fins …
Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces Part 2 CH EN 3453 – Heat Transfer Reminders… • Homework #3 due today • Homework #4 due Friday next week
extended surfaces / fins Convection: Heat transfer between a solid surface and a moving fluid is governed by the Newton’s cooling law: q = hA(Ts-T∞). Therefore, to increase the convective heat transfer, one can Increase the temperature difference (Ts-T∞) between the surface and the fluid.
CFDyna.com Heat Transfer in Extended Surfaces Fins
INTRODUCTION Faculty Server Contact
been discussed and heat transfer through extended surfaces or fins and various methods of increasing heat transfer are discussed. Extended Surface (Fin) are used to enhance convective heat transfer in a wide range of engineering applications and offer a practical means for achieving a large total heat transfer surface area without the use of an excessive amount of primary surface area. Fins
View heattransferfromextendedsurfacesorfins-160904100723.pdf from MECH ME 555 at Southern New Hampshire University. Lectures on Heat Transfer -HEAT TRANSFER FROM
In this study heat transfer performances of extended surfaces (fins) having square, circular, hexagonal, and triangular lateral perforations are studied numerically.
Extended Surfaces/Fins Convection: Heat transfer between a solid surface and a moving fluid is governed by the Newton’s cooling law: q = hA(T
Extended Surfaces (Fins) are widely used in the engineering for getting better heat transfer by providing additional area. In many applications like heat exchangers, for cooling reactor core, electrical transformer, rectifier, etc fins are used for better heat transfer. This work is carried out for find out which material and which cross sectional fin is best suited for the better heat
extended surfaces such as boundary conditions and analysis. Arora et al.[2] in functions in the analysis of extended surface heat transfer and differential equations are formulated from the fundamentals of conduction and convection heat transfer. Rahim et al. [7] in their paper analysed heat transfer through a wall containing triangular fins partially embedded in its volume, Coupled heat
Title: : Heat Transfer Phenomenon of Extended Surfaces in Form of Fins with Internal and External Configurations: A Review PaperId: : 9146 Published in: Internation Journal Of Advance Research And Innovative Ideas In Education
24/03/2017 · 27 videos Play all Heat Transfer: Dr. John Biddle’s Lecture Series CPPMechEngTutorials Thermodynamics and the End of the Universe: Energy, Entropy, and the fundamental laws of physics. – Duration
where T(x) is the temperature of the fin at a particular dimensional position x (refer “Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces” section in [1]). In order to simplify the expression, non-dimensionalize by introducing the following definitions:
What is a Fin? • A fin is a extended surface to increase area for convection heat transfer • Goal is to increase A s to increase • Automobile radiator is example of fin Figure 3-33 from Çengel, Heat Transfer Q&=hAs()Ts −T∞ Q& 10 Innovative Fin Designs Figure 3-34 from Çengel, Heat Transfer • Important application is cooling of power electronics • How do we analyze fin
15/01/2016 · This lecture covers the following topics: 1. Important parameters which affect the heat transfer from surfaces 2. Governing equation for temperature distribution in a fin 3. Infinitely long fin …
– radiation heat transfer from and to the fin is neglected In general, the study of the extended surface heat transfer compromises the movement of the heat within the fin by conduction and the process of the heat exchange between the fin
Heat Transfer from Extended Surface (Fin) A fin is a surface that extends from an object to increase the rate of heat transfer to or from the environment by increase convection. Adding a fin to an object increases the surface area and can sometimes be an economical solution to heat transfer problems.
– If heat is transferred from the surface to the fluid by convection.Nature and Rationale Nature and Rationale of Extended Surfaces • An extended surface (also know as a combined conduction-convection system or a fin) is a solid within which heat transfer …
Fins are used to enhance heat transfer, and the use of fins on a surface cannot be recommended unless the enhancement in heat transfer justifies the added cost and complexity associated with the fins.
Heat transfer from extended surfaces subject to variable
Extended Surfaces/Fins mycsvtunotes.weebly.com
Extended Surfaces (Fins) are widely used in the engineering for getting better heat transfer by providing additional area. In many applications like heat exchangers, for cooling reactor core, electrical transformer, rectifier, etc fins are used for better heat transfer. This work is carried out for find out which material and which cross sectional fin is best suited for the better heat
Updated 10/8/2015. Extended Surfaces (Fins) The normal textbook treatment of heat transfer from fins involves the solution by analytical means of an ordinary differential equation describing transport by conduction along the fin and convection from its surface.
Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces. 1. General Considerations – Extended Surface refers to a solid material in which energy is transferred by conduction within its boundaries and by
Extended surfaces (fins) are one of the heat exchanging devices that are employed extensively to increase heat transfer rates. The rate of heat transfer depends on the surfacearea of the fin
Extended surfaces are extensively used in air-cooled automobile engines, air-conditioning systems, oil industries, computer processors, and other electronic devices. In various applications heat from the fins …
Fins in heat and mass transfer for College students
where T(x) is the temperature of the fin at a particular dimensional position x (refer “Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces” section in [1]). In order to simplify the expression, non-dimensionalize by introducing the following definitions:
Fins as extended surfaces have wide applications in heat transfer augmentation techniques. The solutions are already available in analytical form. This OCTAVE script tries to prepare a plug-and-calculate method for straight fins for all possible combinations of boundary conditions.
– radiation heat transfer from and to the fin is neglected In general, the study of the extended surface heat transfer compromises the movement of the heat within the fin by conduction and the process of the heat exchange between the fin
In the study of heat transfer, fins are surfaces that extend from an object to increase the rate of heat transfer to or from the environment by increasing convection.
Advances and Outlooks of Heat Transfer Enhancement by Longitudinal Vortex Generators such as treated surfaces, rough surfaces, extended surfaces, swirl flow devices, and additives to the fluid, do not require any external powers. On the other hand, the active techniques, such as vibration, electromagnetic field and jet impingement, require external power to enhance heat transfer. In order
2 3/83 Techniques of Heat Transfer Enhan cement and their Application 1. Introduction This chapter discusses enhanced extended surface geometries for the plate-and-fin heat exchanger
Extended surface heat transfer—the Dovetail Fin Request PDF
Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces Thermal Engineering
A fin is a surface that extends from an object to increase the rate of heat transfer to or from the environment by increasing convection heat transfer, The term (extended surface) is commonly used
2 3/83 Techniques of Heat Transfer Enhan cement and their Application 1. Introduction This chapter discusses enhanced extended surface geometries for the plate-and-fin heat exchanger
EXTENDED SURFACES FIN PERFORMANCE FIN EFFICIENCY .Fin Efficiency may be defined as the ratio of actual heat lost by the fin to the maximum heat lost by the fin. The maximum rate at which a fin could dissipate energy, is the rate that would exist, if the entire fin surface were at the base temperature lact Qmax ninc erefore, Qact fin Qmax A. Infinitely Long Fin ml
Advances and Outlooks of Heat Transfer Enhancement by Longitudinal Vortex Generators such as treated surfaces, rough surfaces, extended surfaces, swirl flow devices, and additives to the fluid, do not require any external powers. On the other hand, the active techniques, such as vibration, electromagnetic field and jet impingement, require external power to enhance heat transfer. In order
extended surfaces such as boundary conditions and analysis. Arora et al.[2] in functions in the analysis of extended surface heat transfer and differential equations are formulated from the fundamentals of conduction and convection heat transfer. Rahim et al. [7] in their paper analysed heat transfer through a wall containing triangular fins partially embedded in its volume, Coupled heat
Use of extended surface or fin to enhance heat transfer. Look on the plane side-view of the surface and the surface with fin. The heat transfer rate without the fin from area A to the surrounding fluid is
Heat Transfer from Extended Surface (Fin) A fin is a surface that extends from an object to increase the rate of heat transfer to or from the environment by increase convection. Adding a fin to an object increases the surface area and can sometimes be an economical solution to heat transfer problems.
where T(x) is the temperature of the fin at a particular dimensional position x (refer “Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces” section in [1]). In order to simplify the expression, non-dimensionalize by introducing the following definitions:
Abstract – The main purpose of extended surfaces called fins to increase the heat transfer rate. Many types of fins investigated and different result comes. Both experimentally work or numerically work done by researcher to conclude the results with different types of fins such as rectangular, v-type, notched, unnotched fins with different medium such as water and air to increase the heat
Extended surfaces (fins) are one of the heat exchanging devices that are employed extensively to increase heat transfer rates. The rate of heat transfer depends on the surfacearea of the fin
Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET)
Common Assumptions for Fins •Finned surfaces are commonly used in practice to enhance heat transfer •In the analysis of fins, we consider steady
ONE DIMENSIONAL TRIANGULAR FIN EXPERIMENT
EXTENDED SURFACES / FINS NPTEL
Extended Surfaces (Fins) are widely used in the engineering for getting better heat transfer by providing additional area. In many applications like heat exchangers, for cooling reactor core, electrical transformer, rectifier, etc fins are used for better heat transfer. This work is carried out for find out which material and which cross sectional fin is best suited for the better heat
In this study heat transfer performances of extended surfaces (fins) having square, circular, hexagonal, and triangular lateral perforations are studied numerically.
This paper attempts to provide a comprehensive, coherent, and methodical review of the existing literature on the transient performance of extended surfaces (fins).
The surface area exposed to the surroundings is frequently increased by the attachment of protrusions to the surfaces, and the arrangement provides a means by which heat transfer rate can be substantially improved. The protrusions are called fins or spines, and these extensions can take a variety of forms.
In case of extended surfaces, effective heat transfer area on the side of the extended surface is increased. Passive techniques hold the advantage over the active techniques as they do not require any direct input of external power. These techniques do not require any direct input of external power; rather they use it from the system itself which ultimately leads to an increase in fluid
Title: : Heat Transfer Phenomenon of Extended Surfaces in Form of Fins with Internal and External Configurations: A Review PaperId: : 9146 Published in: Internation Journal Of Advance Research And Innovative Ideas In Education
In the study of heat transfer, fins are surfaces that extend from an object to increase the rate of heat transfer to or from the environment by increasing convection.
Effects of Perforation Geometry on the Heat Transfer
extended surfaces Thermal Conduction Heat Transfer
Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces Part 2 CH EN 3453 – Heat Transfer Reminders… • Homework #3 due today • Homework #4 due Friday next week
24/03/2017 · 27 videos Play all Heat Transfer: Dr. John Biddle’s Lecture Series CPPMechEngTutorials Thermodynamics and the End of the Universe: Energy, Entropy, and the fundamental laws of physics. – Duration
No. 2744 Efficiency of Extended Surfaces with Simultaneous Heat and Mass Transfer A.H. Elmahdy R.C. Biggs ASHRA E Member ABSTRACT An algorithm is presented to determine the efficiency of extended surfaces (circular or
Common Assumptions for Fins •Finned surfaces are commonly used in practice to enhance heat transfer •In the analysis of fins, we consider steady
Heat Transfer for Fins (or Extended Surfaces) Handout Table 3.4 Fin temperature distribution, € θ=T−T ∞, and heat loss, q f, for uniform cross section
This file contains slides on Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces (FINS). The slides were prepared while teaching Heat Transfer course to the M.Tech. students … The slides were prepared while teaching Heat Transfer course to the M.Tech. students …
where T(x) is the temperature of the fin at a particular dimensional position x (refer “Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces” section in [1]). In order to simplify the expression, non-dimensionalize by introducing the following definitions:
Heat Transfer in Extended Surfaces (FINS) Fundamentals
Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces zahurul.buet.ac.bd
The present article investigates the effect of locally variable heat transfer coefficient on the performance of extended surfaces (fins) subject to natural convection. Fins of different profiles have been investigated. The fin profiles presently considered are namely; straight and pin fin with
EXTENDED SURFACES FIN PERFORMANCE FIN EFFICIENCY .Fin Efficiency may be defined as the ratio of actual heat lost by the fin to the maximum heat lost by the fin. The maximum rate at which a fin could dissipate energy, is the rate that would exist, if the entire fin surface were at the base temperature lact Qmax ninc erefore, Qact fin Qmax A. Infinitely Long Fin ml
In case of extended surfaces, effective heat transfer area on the side of the extended surface is increased. Passive techniques hold the advantage over the active techniques as they do not require any direct input of external power. These techniques do not require any direct input of external power; rather they use it from the system itself which ultimately leads to an increase in fluid
Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces. 1. General Considerations – Extended Surface refers to a solid material in which energy is transferred by conduction within its boundaries and by
EXTENDED SURFACES / FINS NPTEL
Heat transfer from extended surfaces subject to variable
The heat flow from a primary surface with fins attached is a combination of the flow from the area of the surface not covered by the fins and the flow through the fins. Therefore knowledge of the temperature distribution through both the primary surface and the attached fins is necessary in order to design the extended surface assembly.
Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces. 1. General Considerations – Extended Surface refers to a solid material in which energy is transferred by conduction within its boundaries and by
In the study of heat transfer, fins are surfaces that extend from an object to increase the rate of heat transfer to or from the environment by increasing convection.
The surface area exposed to the surroundings is frequently increased by the attachment of protrusions to the surfaces, and the arrangement provides a means by which heat transfer rate can be substantially improved. The protrusions are called fins or spines, and these extensions can take a variety of forms.
Fins are used to enhance heat transfer, and the use of fins on a surface cannot be recommended unless the enhancement in heat transfer justifies the added cost and complexity associated with the fins.
The present article investigates the effect of locally variable heat transfer coefficient on the performance of extended surfaces (fins) subject to natural convection. Fins of different profiles have been investigated. The fin profiles presently considered are namely; straight and pin fin with
– If heat is transferred from the surface to the fluid by convection.Nature and Rationale Nature and Rationale of Extended Surfaces • An extended surface (also know as a combined conduction-convection system or a fin) is a solid within which heat transfer …
Title: : Heat Transfer Phenomenon of Extended Surfaces in Form of Fins with Internal and External Configurations: A Review PaperId: : 9146 Published in: Internation Journal Of Advance Research And Innovative Ideas In Education
Advances and Outlooks of Heat Transfer Enhancement by Longitudinal Vortex Generators such as treated surfaces, rough surfaces, extended surfaces, swirl flow devices, and additives to the fluid, do not require any external powers. On the other hand, the active techniques, such as vibration, electromagnetic field and jet impingement, require external power to enhance heat transfer. In order
analysis of the heat transfer growth and the respective pressure drop below a flat surface embedded with ring shaped or circular square perforated fins in a rectangular manner.
Extended Surfaces/Fins Convection: Heat transfer between a solid surface and a moving fluid is governed by the Newton’s cooling law: q = hA(T
24/03/2017 · 27 videos Play all Heat Transfer: Dr. John Biddle’s Lecture Series CPPMechEngTutorials Thermodynamics and the End of the Universe: Energy, Entropy, and the fundamental laws of physics. – …
EXTENDED SURFACES / FINS Convection: Heat transfer between a solid surface and a moving fluid is governed by the Newton’s cooling law: q = hA(T
ONE DIMENSIONAL TRIANGULAR FIN EXPERIMENT
Transient Heat Transfer in Extended Surfaces Applied
transfer surfaces and also the consideration of various performance constraints and parameters of fins (extended surfaces). The primary task of fins employed in highly effective heat exchanger is to increase the heat transfer
View heattransferfromextendedsurfacesorfins-160904100723.pdf from MECH ME 555 at Southern New Hampshire University. Lectures on Heat Transfer -HEAT TRANSFER FROM
24/03/2017 · 27 videos Play all Heat Transfer: Dr. John Biddle’s Lecture Series CPPMechEngTutorials Thermodynamics and the End of the Universe: Energy, Entropy, and the fundamental laws of physics. – Duration
Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET)
Updated 10/8/2015. Extended Surfaces (Fins) The normal textbook treatment of heat transfer from fins involves the solution by analytical means of an ordinary differential equation describing transport by conduction along the fin and convection from its surface.
This file contains slides on Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces (FINS). The slides were prepared while teaching Heat Transfer course to the M.Tech. students … The slides were prepared while teaching Heat Transfer course to the M.Tech. students …
Heat Transfer from Extended Surface (Fin) A fin is a surface that extends from an object to increase the rate of heat transfer to or from the environment by increase convection. Adding a fin to an object increases the surface area and can sometimes be an economical solution to heat transfer problems.
Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces Part 2 CH EN 3453 – Heat Transfer Reminders… • Homework #3 due today • Homework #4 due Friday next week
– If heat is transferred from the surface to the fluid by convection.Nature and Rationale Nature and Rationale of Extended Surfaces • An extended surface (also know as a combined conduction-convection system or a fin) is a solid within which heat transfer …
Title: : Heat Transfer Phenomenon of Extended Surfaces in Form of Fins with Internal and External Configurations: A Review PaperId: : 9146 Published in: Internation Journal Of Advance Research And Innovative Ideas In Education
Heat Transfer for Fins (or Extended Surfaces) Handout
heattransferfromextendedsurfacesorfins-160904100723.pdf
extended surfaces such as boundary conditions and analysis. Arora et al.[2] in functions in the analysis of extended surface heat transfer and differential equations are formulated from the fundamentals of conduction and convection heat transfer. Rahim et al. [7] in their paper analysed heat transfer through a wall containing triangular fins partially embedded in its volume, Coupled heat
This paper attempts to provide a comprehensive, coherent, and methodical review of the existing literature on the transient performance of extended surfaces (fins).
The surface area exposed to the surroundings is frequently increased by the attachment of protrusions to the surfaces, and the arrangement provides a means by which heat transfer rate can be substantially improved. The protrusions are called fins or spines, and these extensions can take a variety of forms.
Title: : Heat Transfer Phenomenon of Extended Surfaces in Form of Fins with Internal and External Configurations: A Review PaperId: : 9146 Published in: Internation Journal Of Advance Research And Innovative Ideas In Education
Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces Part 2 CH EN 3453 – Heat Transfer Reminders… • Homework #3 due today • Homework #4 due Friday next week
This file contains slides on Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces (FINS). The slides were prepared while teaching Heat Transfer course to the M.Tech. students … The slides were prepared while teaching Heat Transfer course to the M.Tech. students …
Extended Surfaces (Fins) are widely used in the engineering for getting better heat transfer by providing additional area. In many applications like heat exchangers, for cooling reactor core, electrical transformer, rectifier, etc fins are used for better heat transfer. This work is carried out for find out which material and which cross sectional fin is best suited for the better heat
2 3/83 Techniques of Heat Transfer Enhan cement and their Application 1. Introduction This chapter discusses enhanced extended surface geometries for the plate-and-fin heat exchanger
Heat and Mass Transfer Heat Transfer Formula Sheet and Tables Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces (Fins) Case I: very long fin Case II: fin with a finite length, L, and the end is insulated Case III: fin with a finite length, L, and losses heat by convection from its end Fin Efficiency: Convection
Extended surfaces are extensively used in air-cooled automobile engines, air-conditioning systems, oil industries, computer processors, and other electronic devices. In various applications heat from the fins …
transfer surfaces and also the consideration of various performance constraints and parameters of fins (extended surfaces). The primary task of fins employed in highly effective heat exchanger is to increase the heat transfer
Fins in heat and mass transfer for College students
Extended surfaces (fins) are one of the heat exchanging devices that are employed extensively to increase heat transfer rates. The rate of heat transfer depends on the surfacearea of the fin
Extended Surfaces (Fins) University of Virginia
Fins Heat Transfer Heat Scribd
Extended Surface Heat Transfer . 3.1 Introduction: Convection: Heat transfer between a solid surface and a moving fluid is governed by the effective surface area by using fins or extended surfaces. Fins are protrusions from the base surface into the cooling fluid, so that the extra surface of the protrusions is also in contact with the fluid. Most of you have encountered cooling fins on
transfer surfaces and also the consideration of various performance constraints and parameters of fins (extended surfaces). The primary task of fins employed in highly effective heat exchanger is to increase the heat transfer
A fin is a surface that extends from an object to increase the rate of heat transfer to or from the environment by increasing convection heat transfer, The term (extended surface) is commonly used
Advances and Outlooks of Heat Transfer Enhancement by Longitudinal Vortex Generators such as treated surfaces, rough surfaces, extended surfaces, swirl flow devices, and additives to the fluid, do not require any external powers. On the other hand, the active techniques, such as vibration, electromagnetic field and jet impingement, require external power to enhance heat transfer. In order
analysis of the heat transfer growth and the respective pressure drop below a flat surface embedded with ring shaped or circular square perforated fins in a rectangular manner.
these cases, certain type of heat exchange surfaces, called extended surfaces, have been developed in which outside area of tube is increased many fold by fins and other appendages. Two types of fins, are in common use viz; longitudinal fins and transverse fins.
extended surfaces Thermal Conduction Heat Transfer
Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces Part 2
Title: : Heat Transfer Phenomenon of Extended Surfaces in Form of Fins with Internal and External Configurations: A Review PaperId: : 9146 Published in: Internation Journal Of Advance Research And Innovative Ideas In Education
extended surfaces / fins Convection: Heat transfer between a solid surface and a moving fluid is governed by the Newton’s cooling law: q = hA(Ts-T∞). Therefore, to increase the convective heat transfer, one can Increase the temperature difference (Ts-T∞) between the surface and the fluid.
Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces. 1. General Considerations – Extended Surface refers to a solid material in which energy is transferred by conduction within its boundaries and by
What is a Fin? • A fin is a extended surface to increase area for convection heat transfer • Goal is to increase A s to increase • Automobile radiator is example of fin Figure 3-33 from Çengel, Heat Transfer Q&=hAs()Ts −T∞ Q& 10 Innovative Fin Designs Figure 3-34 from Çengel, Heat Transfer • Important application is cooling of power electronics • How do we analyze fin
The heat flow from a primary surface with fins attached is a combination of the flow from the area of the surface not covered by the fins and the flow through the fins. Therefore knowledge of the temperature distribution through both the primary surface and the attached fins is necessary in order to design the extended surface assembly.
Extended Surfaces/Fins Convection: Heat transfer between a solid surface and a moving fluid is governed by the Newton’s cooling law: q = hA(T
Keywords Fins, Heat exchanger, Surfaces Abstract A three-dimensional numerical study was conducted to assess the heat transfer perfor- mance of extended fins in a two-row finned tube heat exchanger.
(PDF) Heat transfer from extended surfaces subject to
Effects of Perforation Geometry on the Heat Transfer
– If heat is transferred from the surface to the fluid by convection.Nature and Rationale Nature and Rationale of Extended Surfaces • An extended surface (also know as a combined conduction-convection system or a fin) is a solid within which heat transfer …
extended surfaces such as boundary conditions and analysis. Arora et al.[2] in functions in the analysis of extended surface heat transfer and differential equations are formulated from the fundamentals of conduction and convection heat transfer. Rahim et al. [7] in their paper analysed heat transfer through a wall containing triangular fins partially embedded in its volume, Coupled heat
Fins as extended surfaces have wide applications in heat transfer augmentation techniques. The solutions are already available in analytical form. This OCTAVE script tries to prepare a plug-and-calculate method for straight fins for all possible combinations of boundary conditions.
15/01/2016 · This lecture covers the following topics: 1. Important parameters which affect the heat transfer from surfaces 2. Governing equation for temperature distribution in a fin 3. Infinitely long fin …
No. 2744 Efficiency of Extended Surfaces with Simultaneous Heat and Mass Transfer A.H. Elmahdy R.C. Biggs ASHRA E Member ABSTRACT An algorithm is presented to determine the efficiency of extended surfaces (circular or
In this study heat transfer performances of extended surfaces (fins) having square, circular, hexagonal, and triangular lateral perforations are studied numerically.
Abstract – The main purpose of extended surfaces called fins to increase the heat transfer rate. Many types of fins investigated and different result comes. Both experimentally work or numerically work done by researcher to conclude the results with different types of fins such as rectangular, v-type, notched, unnotched fins with different medium such as water and air to increase the heat
The heat transfer characteristics of fins are known as conduction-convection systems. Consider a cylindrical fin with a heat source located at its base and its surface is exposed to a surrounding.
Heat transfer inside fin systems composed of primary rectangular fins with large number of slender rods attached on their surfaces is modeled and analyzed analytically in this work. The
Extended surfaces are extensively used in air-cooled automobile engines, air-conditioning systems, oil industries, computer processors, and other electronic devices. In various applications heat from the fins …
Common Assumptions for Fins •Finned surfaces are commonly used in practice to enhance heat transfer •In the analysis of fins, we consider steady
Extended Surfaces (Fins) University of Virginia
Heat transfer from extended surfaces (or fins) SlideShare
Fins are used to enhance heat transfer, and the use of fins on a surface cannot be recommended unless the enhancement in heat transfer justifies the added cost and complexity associated with the fins.
Extended Surface Heat Transfer . 3.1 Introduction: Convection: Heat transfer between a solid surface and a moving fluid is governed by the effective surface area by using fins or extended surfaces. Fins are protrusions from the base surface into the cooling fluid, so that the extra surface of the protrusions is also in contact with the fluid. Most of you have encountered cooling fins on
24/03/2017 · 27 videos Play all Heat Transfer: Dr. John Biddle’s Lecture Series CPPMechEngTutorials Thermodynamics and the End of the Universe: Energy, Entropy, and the fundamental laws of physics. – Duration
The heat transfer characteristics of fins are known as conduction-convection systems. Consider a cylindrical fin with a heat source located at its base and its surface is exposed to a surrounding.
In the study of heat transfer, fins are surfaces that extend from an object to increase the rate of heat transfer to or from the environment by increasing convection.
analysis of the heat transfer growth and the respective pressure drop below a flat surface embedded with ring shaped or circular square perforated fins in a rectangular manner.
EXTENDED SURFACES / FINS NPTEL
Advances and Outlooks of Heat Transfer Enhancement by Longitudinal Vortex Generators such as treated surfaces, rough surfaces, extended surfaces, swirl flow devices, and additives to the fluid, do not require any external powers. On the other hand, the active techniques, such as vibration, electromagnetic field and jet impingement, require external power to enhance heat transfer. In order
Heat Transfer from Extended Surfaces Thermal Engineering
Extended Surfaces / Fins Heat Transfer Convection
Fins and Extended Surfaces Heat Transfer Applications
transfer surfaces and also the consideration of various performance constraints and parameters of fins (extended surfaces). The primary task of fins employed in highly effective heat exchanger is to increase the heat transfer
Heat transfer through extended surfaces(fins) Heat
(PDF) Heat transfer from extended surfaces subject to