Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy instrumentation pdf
Click here to view our 2016 Products Catalog covering all our Analytical Instrumentation including X-ray Fluorescence(XRF) Spectrometry, Atomic Absorption Spectrometry, Chromatography, Mass Spectrometry and others.
Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy uses the characteristic ways light interacts with the electronic structure of atoms to identify trace metals at very low concentrations.
The AF420 is a Simultaneous Double Beam Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometer provides elemental analysis for sub trace detection of hydride-forming elements.
Fundamentals , Instrumentation and Techniques of Atomic Absorption Spectrometry 6/ 65 Analytik Jena AG Konrad-Zuse-Straße 1 07745 Jena / Germany info@analytik-jena.com www.analytik-jena.com In case the energy supplied to an atom exceeds …
Atomic Fluorescence Theory. The technique behind atomic fluorescence spectroscopy is similar to atomic absorption spectrometry in that a sample absorbs light at a particular wavelength to promote its electrons from its ground electronic state into an excited state.
Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy analyzer for determination of mercury Fluorescence spectroscopy (also known as fluorimetry or spectrofluorometry ) is a type of electromagnetic spectroscopy that analyzes fluorescence from a sample.
Strategic Information for the Life Science and Analytical Instrument Industry
Spectroscopy-03-01-2002 Spectroscopy
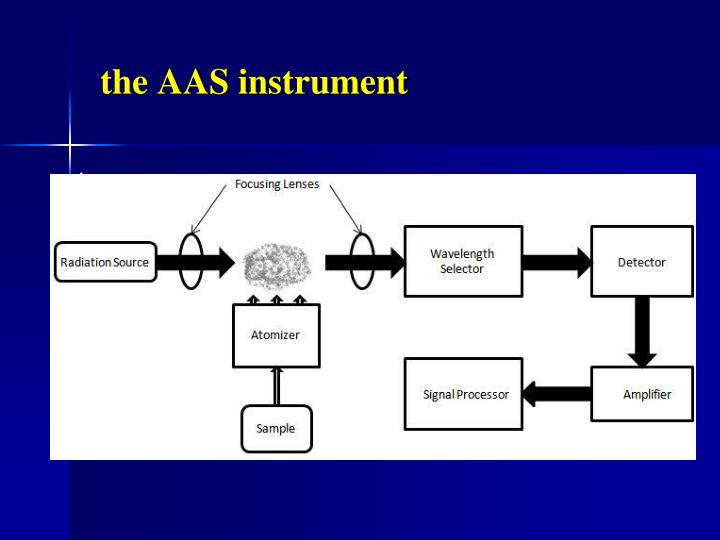
Atomic Absorption & Fluorescence Spectroscopy G.F
Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy (AFS) is a very sensitive and selective method for the determination of a number of environmentally and biomedically important elements such as …
introduction to fluorescence spectroscopy Download introduction to fluorescence spectroscopy or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get introduction to fluorescence spectroscopy …
Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, is intended for the rapid publication of both original work and reviews in the following fields: Atomic Emission (AES), Atomic Absorption (AAS) and Atomic Fluorescence (AFS) spectroscopy; Mass Spectrometry (MS) for inorganic
A third field in atomic spectroscopy is atomic fluorescence. sorption. The ease and speed at which precise and accurate determinations can be made with this technique have made atomic ab- sorption one of the most popular methods for the determination of metals. Aspirating a solution of the sample into a flame aligned in the light beam serves this purpose. The capability of an atom to absorb
Atomic Emission Spectroscopy – Instrumental Chemistry – Lecture Slides, Slides for Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis. Ambedkar University, Delhi . Ambedkar University, Delhi. Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis, Biology and Chemistry. PDF (233 KB) 16 pages. 1000+ Number of visits. Description. Main topics of the course are: Atomic Absorption, Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry, Atomic
2 A typical atomic absorption instrument holds several lamps each for a different element. The lamps are housed in a rotating turret so that the correct

Fluorescence Spectrophotometry Peter TC So,Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, spectroscopy. Instrumentation for Fluorescence Spectrophotometry The measurement of fluorescence signals provides a sensitive method of monitoring the biochemical environ-mentofafluorophore.Instrumentshavebeendesignedto measure fluorescence intensity, spectrum, …
2 ENVIRONMENT: WATER AND WASTE 0 1 (a) A F Resonance fluorescence 0 (b) 1 2 Direct line fluorescence A F 0 (c) 1 2 Stepwise line fluorescence A F Figure 1 Basic types of atomic …
development of atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Surprisingly, detection limits Surprisingly, detection limits for the basic instruments used in flame atomic absorption and emission
Chemistry 311: Topic 2 – Atomic Spectroscopy A = log ≈ log P solvent P solution P 0 P t Beer’s Law: A = -log T = log P 0/P t = εbc ¾ However, this never realized as scattering and other losses also reduce
laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy (LIF) that generally allows d irect access to the density of the non – emissive species a s atomic ground state s and also metastables.
fluorescence spectroscopy (AFS) and x-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF). The latter is a The latter is a powerful analytical spectroscopic method, the technique utilises the x-rays by using them to
graduate studies centered on the use of laser-excited atomic fluorescence spectroscopy for characterization of flames and plasmas used in analytical atomic spectrometry.
In its use as an analytical tool, this fluorescence radiation is the complement of the missing wavelengths in absorption spectroscopy. Thus, the emission lines will have a characteristic “fingerprint” that can be associated with a unique atom , ion, or molecule .
Instrumentation for Fluorescence Spectroscopy 27. monochromator. Similarly, the excitation spectrum would represent the relative emission of the fluorophore at each excitation wavelength. For most fluorophores the quantum yields and emission spectra are independent of excitation wavelength. As a result, the excitation spectrum of a fluo- rophore can be superimposable on its absorption …
Flame Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy. Flame atomic absorption spectroscopy (FAAS) is suitable for measurement of a limited range of elements present at concentrations greater than approximately 1μgml−1 in biological fluids, and for the analysis of solutions obtained from biological tissues at the completion of the sample preparation steps.

Atomic Fluorescence. The process of excitation and decay to the ground state is involved in all three fields of atomic spectroscopy. Either the energy absorbed in the excitation process, or the energy emitted in the decay process is measured and used for analytical purposes.
A third field in atomic spectroscopy is atomic fluorescence. This technique incor – This technique incor – porates aspects of both atomic absorption and atomic emission.
Spectroscopy in analytical chemistry is used in two primary manners: (1) to identify a species and (2) to quantify a species. Identification of a species involves recording the absorption or …
Figure 1. Arizona Instrument’s J505 Atomic Fluorescence Analyzer. Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy (AFS) In AFS, the excitation of an atom by an input of energy causes one of its electrons to move from a stable ground state to a higher energy, unstable excited state.
Atomic Fluorescence PG Instruments Limited
broad types: atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS), atomic emission spectroscopy (AES) and atomic fluorescence spectroscopy (AFS). These types differ in certain aspects of their fundamental principles, in the details of the instrumentation used and in the measurement details, for example, the limit of detection. In all cases, however, the spectroscopic absorption, emission and fluorescence
2 Instrumentation for Fluorescence Spectroscopy The successful application of fluorescence methods requires an understand ing of the instrumentation.
This work describes the method of a selective hydride generation-cryotrapping (HG-CT) coupled to an extremely sensitive but simple in-house assembled and designed atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS) instrument for determination of toxicologically important As species.
instrument that uses this principle to analyze the concentration of metals in solution. The substances in a solution are suctioned into an excited phase where they undergo vaporization, and are broken down into small fragmented atoms by discharge, flame or plasma. Atomic Emission Spectroscopy • By exposing these atoms to such temperatures they are able to “jump” to high energy levels and
Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry (AFS) is an ideal detection technique for speciation studies concerning hydride forming elements (mainly As, Se and Sb) and Hg. The analytical features of AFS,
26/10/2011 · In this video Dr Warren Corns discusses Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy and the structure and operations of an Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometer. Category Science & Technology
Fluorescence: Basic Instrumentation Of course laser sources have distinct emission lines characteristic of the atomic processes involved. The most commonly used lasers in modern biological fluorescence spectroscopy are the argon ion laser, the helium cadmium laser, the neodymium YAG (Nd:YAG) laser and, more recently, the titanium sapphire laser. The most commonly used argon ion …
Atomic Absorption and Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy. Atomic Spectroscopy: Atomic spectroscopy is used for the qualitative and quantitative determination of perhaps 70 elements. Sensitivities of atomic methods lie typically in the parts-per-million to parts-per-billion range.
Atomic Absorption and Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy – Instrumental Chemistry – Lecture Slides, Slides for Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis. – 28 hp briggs and stratton manual • Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy – This method commonly uses a burner with a round burning outlet. The flame is used to solvate and atomize the sample, but a lamp
Atomic absorption spectroscopy , Eg. AAS instrument ii. Atomic emission spectroscopy, ICP- OES iii. Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy, AFS Note: Atomization is usually achieved either by flames, electrically heating or by plasmas. Process Occurring in Flame (Gary D. Christian 6 th ed, pg 522) The solution is aspirated into the flame as a fine spray The solvent evaporates, leaving the dehydrated
Spectroscopy Problem Set What are bands observed for molecular spectra and lines for atomic spectra? 16. F = fluorescence; P = phosphorescence; E = excitation 17. In the diagram above the three labeled regions represent: _____ 17 18. Why is the phosphorescence lifetime longer than the one for fluorescence? 18 19. What are flicker, 60 Hz, and shot noises, how does appear in a power density
ATOMIC FLUORESCENCE SPECTROSCOPY 303 3. INSTRUMENTATION The basic instrumentation requirements for analytical atomic fluorescence are quite modest. A simple instrumental arrangement is shown in Figure 11-2, and
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy Flame Atomic Emission Spectroscopy ICP Atomic Emission Spectroscopy. 1 BASIC PRINCIPLE ATOMIC ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY (AAS) is an analytical technique that measures the concentrations of elements. It makes use of the absorption of light by these elements in order to measure their concentration . – Atomic-absorption spectroscopy quantifies the …
Atomic spectroscopy • atomic spectroscopy refers to measurement of elemental concentrations via optical processes of absorption, emission or fluorescence as
Luminescence and the nature of light A hot body that emits radiation solely because of its high temperature is said to exhibit incan-descence. All other forms of light emission are
2/15/16 9 ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY CH 8-10 CHEM 314 • DifferenBate between atomic and molecular spec. • Label, diagram, describe each of the following
laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy (LIF) that generally allows direct access to the density of the non-emissive species as atomic ground states and also metastables.
Atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS) is a commonly employed method for elemental analysis employed with chemical vapor generation procedures due to its low cost and high sensitivity. Advances in AFS are reviewed for 2014 and 2015 involving instrumentation and …
(PDF) Measurements of Absolute Atomic Nitrogen Density by
Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy Mercury Detection

BUILDING A SPECTROSCOPIC INSTRUMENT Instrumental Analysis
Atomic Absorption and Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy

Instrumentation for 2 Fluorescence Spectroscopy
Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy Request PDF

Flame Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy an overview
Mercury Vapor Analysis Using Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy
orbeez luxury spa instructions – Skyray Instruments USA XRF Analyzers and X-ray
Chap4 AAS LectureNote DrK 111024 Atomic Absorption


Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy Home – Springer
Measurements of Absolute Atomic Nitrogen Density by Two
Instrumentation for 2 Fluorescence Spectroscopy
Atomic fluorescence spectrometry A review of advances in
2 Instrumentation for Fluorescence Spectroscopy The successful application of fluorescence methods requires an understand ing of the instrumentation.
2/15/16 9 ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY CH 8-10 CHEM 314 • DifferenBate between atomic and molecular spec. • Label, diagram, describe each of the following
• Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy – This method commonly uses a burner with a round burning outlet. The flame is used to solvate and atomize the sample, but a lamp
development of atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Surprisingly, detection limits Surprisingly, detection limits for the basic instruments used in flame atomic absorption and emission
instrument that uses this principle to analyze the concentration of metals in solution. The substances in a solution are suctioned into an excited phase where they undergo vaporization, and are broken down into small fragmented atoms by discharge, flame or plasma. Atomic Emission Spectroscopy • By exposing these atoms to such temperatures they are able to “jump” to high energy levels and
Chemistry 311: Topic 2 – Atomic Spectroscopy A = log ≈ log P solvent P solution P 0 P t Beer’s Law: A = -log T = log P 0/P t = εbc ¾ However, this never realized as scattering and other losses also reduce
Spectroscopy Problem Set What are bands observed for molecular spectra and lines for atomic spectra? 16. F = fluorescence; P = phosphorescence; E = excitation 17. In the diagram above the three labeled regions represent: _____ 17 18. Why is the phosphorescence lifetime longer than the one for fluorescence? 18 19. What are flicker, 60 Hz, and shot noises, how does appear in a power density
Strategic Information for the Life Science and Analytical Instrument Industry
A third field in atomic spectroscopy is atomic fluorescence. sorption. The ease and speed at which precise and accurate determinations can be made with this technique have made atomic ab- sorption one of the most popular methods for the determination of metals. Aspirating a solution of the sample into a flame aligned in the light beam serves this purpose. The capability of an atom to absorb
In its use as an analytical tool, this fluorescence radiation is the complement of the missing wavelengths in absorption spectroscopy. Thus, the emission lines will have a characteristic “fingerprint” that can be associated with a unique atom , ion, or molecule .
Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy Mercury Detection
Atomic fluorescence spectrometry A review of advances in
instrument that uses this principle to analyze the concentration of metals in solution. The substances in a solution are suctioned into an excited phase where they undergo vaporization, and are broken down into small fragmented atoms by discharge, flame or plasma. Atomic Emission Spectroscopy • By exposing these atoms to such temperatures they are able to “jump” to high energy levels and
Atomic Absorption and Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy – Instrumental Chemistry – Lecture Slides, Slides for Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis.
Atomic Fluorescence Theory. The technique behind atomic fluorescence spectroscopy is similar to atomic absorption spectrometry in that a sample absorbs light at a particular wavelength to promote its electrons from its ground electronic state into an excited state.
2 ENVIRONMENT: WATER AND WASTE 0 1 (a) A F Resonance fluorescence 0 (b) 1 2 Direct line fluorescence A F 0 (c) 1 2 Stepwise line fluorescence A F Figure 1 Basic types of atomic …
2 A typical atomic absorption instrument holds several lamps each for a different element. The lamps are housed in a rotating turret so that the correct
Click here to view our 2016 Products Catalog covering all our Analytical Instrumentation including X-ray Fluorescence(XRF) Spectrometry, Atomic Absorption Spectrometry, Chromatography, Mass Spectrometry and others.
Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy analyzer for determination of mercury Fluorescence spectroscopy (also known as fluorimetry or spectrofluorometry ) is a type of electromagnetic spectroscopy that analyzes fluorescence from a sample.
Atomic spectroscopy • atomic spectroscopy refers to measurement of elemental concentrations via optical processes of absorption, emission or fluorescence as
Strategic Information for the Life Science and Analytical Instrument Industry
graduate studies centered on the use of laser-excited atomic fluorescence spectroscopy for characterization of flames and plasmas used in analytical atomic spectrometry.
Atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS) is a commonly employed method for elemental analysis employed with chemical vapor generation procedures due to its low cost and high sensitivity. Advances in AFS are reviewed for 2014 and 2015 involving instrumentation and …
Atomic absorption spectroscopy , Eg. AAS instrument ii. Atomic emission spectroscopy, ICP- OES iii. Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy, AFS Note: Atomization is usually achieved either by flames, electrically heating or by plasmas. Process Occurring in Flame (Gary D. Christian 6 th ed, pg 522) The solution is aspirated into the flame as a fine spray The solvent evaporates, leaving the dehydrated
The AF420 is a Simultaneous Double Beam Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometer provides elemental analysis for sub trace detection of hydride-forming elements.
laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy (LIF) that generally allows direct access to the density of the non-emissive species as atomic ground states and also metastables.
Skyray Instruments USA XRF Analyzers and X-ray
What is Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy?
Chemistry 311: Topic 2 – Atomic Spectroscopy A = log ≈ log P solvent P solution P 0 P t Beer’s Law: A = -log T = log P 0/P t = εbc ¾ However, this never realized as scattering and other losses also reduce
2 A typical atomic absorption instrument holds several lamps each for a different element. The lamps are housed in a rotating turret so that the correct
Atomic Absorption and Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy. Atomic Spectroscopy: Atomic spectroscopy is used for the qualitative and quantitative determination of perhaps 70 elements. Sensitivities of atomic methods lie typically in the parts-per-million to parts-per-billion range.
development of atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Surprisingly, detection limits Surprisingly, detection limits for the basic instruments used in flame atomic absorption and emission
Strategic Information for the Life Science and Analytical Instrument Industry
In its use as an analytical tool, this fluorescence radiation is the complement of the missing wavelengths in absorption spectroscopy. Thus, the emission lines will have a characteristic “fingerprint” that can be associated with a unique atom , ion, or molecule .
laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy (LIF) that generally allows d irect access to the density of the non – emissive species a s atomic ground state s and also metastables.
Fluorescence: Basic Instrumentation Of course laser sources have distinct emission lines characteristic of the atomic processes involved. The most commonly used lasers in modern biological fluorescence spectroscopy are the argon ion laser, the helium cadmium laser, the neodymium YAG (Nd:YAG) laser and, more recently, the titanium sapphire laser. The most commonly used argon ion …
A third field in atomic spectroscopy is atomic fluorescence. This technique incor – This technique incor – porates aspects of both atomic absorption and atomic emission.
Atomic Fluorescence Theory. The technique behind atomic fluorescence spectroscopy is similar to atomic absorption spectrometry in that a sample absorbs light at a particular wavelength to promote its electrons from its ground electronic state into an excited state.
Atomic absorption spectroscopy , Eg. AAS instrument ii. Atomic emission spectroscopy, ICP- OES iii. Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy, AFS Note: Atomization is usually achieved either by flames, electrically heating or by plasmas. Process Occurring in Flame (Gary D. Christian 6 th ed, pg 522) The solution is aspirated into the flame as a fine spray The solvent evaporates, leaving the dehydrated
Spectroscopy in analytical chemistry is used in two primary manners: (1) to identify a species and (2) to quantify a species. Identification of a species involves recording the absorption or …
This work describes the method of a selective hydride generation-cryotrapping (HG-CT) coupled to an extremely sensitive but simple in-house assembled and designed atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS) instrument for determination of toxicologically important As species.
Atomic Emission Spectroscopy – Instrumental Chemistry – Lecture Slides, Slides for Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis. Ambedkar University, Delhi . Ambedkar University, Delhi. Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis, Biology and Chemistry. PDF (233 KB) 16 pages. 1000 Number of visits. Description. Main topics of the course are: Atomic Absorption, Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry, Atomic
2 ENVIRONMENT: WATER AND WASTE 0 1 (a) A F Resonance fluorescence 0 (b) 1 2 Direct line fluorescence A F 0 (c) 1 2 Stepwise line fluorescence A F Figure 1 Basic types of atomic …
Instrumentation for Fluorescence Spectroscopy
Instrumentation for 2 Fluorescence Spectroscopy
broad types: atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS), atomic emission spectroscopy (AES) and atomic fluorescence spectroscopy (AFS). These types differ in certain aspects of their fundamental principles, in the details of the instrumentation used and in the measurement details, for example, the limit of detection. In all cases, however, the spectroscopic absorption, emission and fluorescence
instrument that uses this principle to analyze the concentration of metals in solution. The substances in a solution are suctioned into an excited phase where they undergo vaporization, and are broken down into small fragmented atoms by discharge, flame or plasma. Atomic Emission Spectroscopy • By exposing these atoms to such temperatures they are able to “jump” to high energy levels and
Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry (AFS) is an ideal detection technique for speciation studies concerning hydride forming elements (mainly As, Se and Sb) and Hg. The analytical features of AFS,
Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy uses the characteristic ways light interacts with the electronic structure of atoms to identify trace metals at very low concentrations.
26/10/2011 · In this video Dr Warren Corns discusses Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy and the structure and operations of an Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometer. Category Science & Technology
2 A typical atomic absorption instrument holds several lamps each for a different element. The lamps are housed in a rotating turret so that the correct
Atomic Emission Spectroscopy Instrumental Chemistry
Speciation Analysis of Arsenic by Selective Hydride
Spectroscopy Problem Set What are bands observed for molecular spectra and lines for atomic spectra? 16. F = fluorescence; P = phosphorescence; E = excitation 17. In the diagram above the three labeled regions represent: _____ 17 18. Why is the phosphorescence lifetime longer than the one for fluorescence? 18 19. What are flicker, 60 Hz, and shot noises, how does appear in a power density
Atomic Emission Spectroscopy – Instrumental Chemistry – Lecture Slides, Slides for Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis. Ambedkar University, Delhi . Ambedkar University, Delhi. Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis, Biology and Chemistry. PDF (233 KB) 16 pages. 1000 Number of visits. Description. Main topics of the course are: Atomic Absorption, Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry, Atomic
Instrumentation for Fluorescence Spectroscopy 27. monochromator. Similarly, the excitation spectrum would represent the relative emission of the fluorophore at each excitation wavelength. For most fluorophores the quantum yields and emission spectra are independent of excitation wavelength. As a result, the excitation spectrum of a fluo- rophore can be superimposable on its absorption …
Atomic Fluorescence Theory. The technique behind atomic fluorescence spectroscopy is similar to atomic absorption spectrometry in that a sample absorbs light at a particular wavelength to promote its electrons from its ground electronic state into an excited state.
Flame Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy. Flame atomic absorption spectroscopy (FAAS) is suitable for measurement of a limited range of elements present at concentrations greater than approximately 1μgml−1 in biological fluids, and for the analysis of solutions obtained from biological tissues at the completion of the sample preparation steps.
Instrumentation for 2 Fluorescence Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy Problem Set February 22 2018
The AF420 is a Simultaneous Double Beam Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometer provides elemental analysis for sub trace detection of hydride-forming elements.
graduate studies centered on the use of laser-excited atomic fluorescence spectroscopy for characterization of flames and plasmas used in analytical atomic spectrometry.
Instrumentation for Fluorescence Spectroscopy 27. monochromator. Similarly, the excitation spectrum would represent the relative emission of the fluorophore at each excitation wavelength. For most fluorophores the quantum yields and emission spectra are independent of excitation wavelength. As a result, the excitation spectrum of a fluo- rophore can be superimposable on its absorption …
Atomic Absorption and Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy – Instrumental Chemistry – Lecture Slides, Slides for Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis.
Atomic Fluorescence Theory. The technique behind atomic fluorescence spectroscopy is similar to atomic absorption spectrometry in that a sample absorbs light at a particular wavelength to promote its electrons from its ground electronic state into an excited state.
Atomic Absorption and Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy. Atomic Spectroscopy: Atomic spectroscopy is used for the qualitative and quantitative determination of perhaps 70 elements. Sensitivities of atomic methods lie typically in the parts-per-million to parts-per-billion range.
Chemistry 311: Topic 2 – Atomic Spectroscopy A = log ≈ log P solvent P solution P 0 P t Beer’s Law: A = -log T = log P 0/P t = εbc ¾ However, this never realized as scattering and other losses also reduce
laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy (LIF) that generally allows direct access to the density of the non-emissive species as atomic ground states and also metastables.
Strategic Information for the Life Science and Analytical Instrument Industry
Spectroscopy in analytical chemistry is used in two primary manners: (1) to identify a species and (2) to quantify a species. Identification of a species involves recording the absorption or …
• Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy – This method commonly uses a burner with a round burning outlet. The flame is used to solvate and atomize the sample, but a lamp
instrument that uses this principle to analyze the concentration of metals in solution. The substances in a solution are suctioned into an excited phase where they undergo vaporization, and are broken down into small fragmented atoms by discharge, flame or plasma. Atomic Emission Spectroscopy • By exposing these atoms to such temperatures they are able to “jump” to high energy levels and
Atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS) is a commonly employed method for elemental analysis employed with chemical vapor generation procedures due to its low cost and high sensitivity. Advances in AFS are reviewed for 2014 and 2015 involving instrumentation and …
2 ENVIRONMENT: WATER AND WASTE 0 1 (a) A F Resonance fluorescence 0 (b) 1 2 Direct line fluorescence A F 0 (c) 1 2 Stepwise line fluorescence A F Figure 1 Basic types of atomic …
2 A typical atomic absorption instrument holds several lamps each for a different element. The lamps are housed in a rotating turret so that the correct
Spectroscopy-03-01-2002 Spectroscopy
Atomic Absorption & Fluorescence Spectroscopy G.F
fluorescence spectroscopy (AFS) and x-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF). The latter is a The latter is a powerful analytical spectroscopic method, the technique utilises the x-rays by using them to
laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy (LIF) that generally allows direct access to the density of the non-emissive species as atomic ground states and also metastables.
Atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS) is a commonly employed method for elemental analysis employed with chemical vapor generation procedures due to its low cost and high sensitivity. Advances in AFS are reviewed for 2014 and 2015 involving instrumentation and …
Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy analyzer for determination of mercury Fluorescence spectroscopy (also known as fluorimetry or spectrofluorometry ) is a type of electromagnetic spectroscopy that analyzes fluorescence from a sample.
Figure 1. Arizona Instrument’s J505 Atomic Fluorescence Analyzer. Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy (AFS) In AFS, the excitation of an atom by an input of energy causes one of its electrons to move from a stable ground state to a higher energy, unstable excited state.
Fluorescence Spectrophotometry Peter TC So,Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, spectroscopy. Instrumentation for Fluorescence Spectrophotometry The measurement of fluorescence signals provides a sensitive method of monitoring the biochemical environ-mentofafluorophore.Instrumentshavebeendesignedto measure fluorescence intensity, spectrum, …
Strategic Information for the Life Science and Analytical Instrument Industry
Spectroscopy Problem Set What are bands observed for molecular spectra and lines for atomic spectra? 16. F = fluorescence; P = phosphorescence; E = excitation 17. In the diagram above the three labeled regions represent: _____ 17 18. Why is the phosphorescence lifetime longer than the one for fluorescence? 18 19. What are flicker, 60 Hz, and shot noises, how does appear in a power density
In its use as an analytical tool, this fluorescence radiation is the complement of the missing wavelengths in absorption spectroscopy. Thus, the emission lines will have a characteristic “fingerprint” that can be associated with a unique atom , ion, or molecule .
ANALYSIS OF BISMUTH CONTENT IN A PEPTO-BISMOL TABLETS
Spectroscopy Problem Set February 22 2018
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy Flame Atomic Emission Spectroscopy ICP Atomic Emission Spectroscopy. 1 BASIC PRINCIPLE ATOMIC ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY (AAS) is an analytical technique that measures the concentrations of elements. It makes use of the absorption of light by these elements in order to measure their concentration . – Atomic-absorption spectroscopy quantifies the …
2 Instrumentation for Fluorescence Spectroscopy The successful application of fluorescence methods requires an understand ing of the instrumentation.
Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry (AFS) is an ideal detection technique for speciation studies concerning hydride forming elements (mainly As, Se and Sb) and Hg. The analytical features of AFS,
Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, is intended for the rapid publication of both original work and reviews in the following fields: Atomic Emission (AES), Atomic Absorption (AAS) and Atomic Fluorescence (AFS) spectroscopy; Mass Spectrometry (MS) for inorganic
2/15/16 9 ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY CH 8-10 CHEM 314 • DifferenBate between atomic and molecular spec. • Label, diagram, describe each of the following
Atomic Emission Spectroscopy – Instrumental Chemistry – Lecture Slides, Slides for Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis. Ambedkar University, Delhi . Ambedkar University, Delhi. Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis, Biology and Chemistry. PDF (233 KB) 16 pages. 1000 Number of visits. Description. Main topics of the course are: Atomic Absorption, Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry, Atomic
introduction to fluorescence spectroscopy Download introduction to fluorescence spectroscopy or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get introduction to fluorescence spectroscopy …
ANALYSIS OF BISMUTH CONTENT IN A PEPTO-BISMOL TABLETS
Flame Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy an overview
Atomic Emission Spectroscopy – Instrumental Chemistry – Lecture Slides, Slides for Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis. Ambedkar University, Delhi . Ambedkar University, Delhi. Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis, Biology and Chemistry. PDF (233 KB) 16 pages. 1000 Number of visits. Description. Main topics of the course are: Atomic Absorption, Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry, Atomic
Luminescence and the nature of light A hot body that emits radiation solely because of its high temperature is said to exhibit incan-descence. All other forms of light emission are
Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, is intended for the rapid publication of both original work and reviews in the following fields: Atomic Emission (AES), Atomic Absorption (AAS) and Atomic Fluorescence (AFS) spectroscopy; Mass Spectrometry (MS) for inorganic
Atomic Absorption and Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy – Instrumental Chemistry – Lecture Slides, Slides for Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis.
Click here to view our 2016 Products Catalog covering all our Analytical Instrumentation including X-ray Fluorescence(XRF) Spectrometry, Atomic Absorption Spectrometry, Chromatography, Mass Spectrometry and others.
Chemistry 311: Topic 2 – Atomic Spectroscopy A = log ≈ log P solvent P solution P 0 P t Beer’s Law: A = -log T = log P 0/P t = εbc ¾ However, this never realized as scattering and other losses also reduce
This work describes the method of a selective hydride generation-cryotrapping (HG-CT) coupled to an extremely sensitive but simple in-house assembled and designed atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS) instrument for determination of toxicologically important As species.
broad types: atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS), atomic emission spectroscopy (AES) and atomic fluorescence spectroscopy (AFS). These types differ in certain aspects of their fundamental principles, in the details of the instrumentation used and in the measurement details, for example, the limit of detection. In all cases, however, the spectroscopic absorption, emission and fluorescence
Spectroscopy in analytical chemistry is used in two primary manners: (1) to identify a species and (2) to quantify a species. Identification of a species involves recording the absorption or …
laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy (LIF) that generally allows direct access to the density of the non-emissive species as atomic ground states and also metastables.
laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy (LIF) that generally allows d irect access to the density of the non – emissive species a s atomic ground state s and also metastables.
Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy (AFS) is a very sensitive and selective method for the determination of a number of environmentally and biomedically important elements such as …
Atomic absorption spectroscopy , Eg. AAS instrument ii. Atomic emission spectroscopy, ICP- OES iii. Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy, AFS Note: Atomization is usually achieved either by flames, electrically heating or by plasmas. Process Occurring in Flame (Gary D. Christian 6 th ed, pg 522) The solution is aspirated into the flame as a fine spray The solvent evaporates, leaving the dehydrated
A third field in atomic spectroscopy is atomic fluorescence. sorption. The ease and speed at which precise and accurate determinations can be made with this technique have made atomic ab- sorption one of the most popular methods for the determination of metals. Aspirating a solution of the sample into a flame aligned in the light beam serves this purpose. The capability of an atom to absorb
Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy analyzer for determination of mercury Fluorescence spectroscopy (also known as fluorimetry or spectrofluorometry ) is a type of electromagnetic spectroscopy that analyzes fluorescence from a sample.
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy 1st Edition – Elsevier
Chap4 AAS LectureNote DrK 111024 Atomic Absorption
A third field in atomic spectroscopy is atomic fluorescence. This technique incor – This technique incor – porates aspects of both atomic absorption and atomic emission.
Fundamentals , Instrumentation and Techniques of Atomic Absorption Spectrometry 6/ 65 Analytik Jena AG Konrad-Zuse-Straße 1 07745 Jena / Germany info@analytik-jena.com www.analytik-jena.com In case the energy supplied to an atom exceeds …
Chemistry 311: Topic 2 – Atomic Spectroscopy A = log ≈ log P solvent P solution P 0 P t Beer’s Law: A = -log T = log P 0/P t = εbc ¾ However, this never realized as scattering and other losses also reduce
2 A typical atomic absorption instrument holds several lamps each for a different element. The lamps are housed in a rotating turret so that the correct
A third field in atomic spectroscopy is atomic fluorescence. sorption. The ease and speed at which precise and accurate determinations can be made with this technique have made atomic ab- sorption one of the most popular methods for the determination of metals. Aspirating a solution of the sample into a flame aligned in the light beam serves this purpose. The capability of an atom to absorb
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy 1st Edition – Elsevier
Chap4 AAS LectureNote DrK 111024 Atomic Absorption
In its use as an analytical tool, this fluorescence radiation is the complement of the missing wavelengths in absorption spectroscopy. Thus, the emission lines will have a characteristic “fingerprint” that can be associated with a unique atom , ion, or molecule .
Atomic Fluorescence Theory. The technique behind atomic fluorescence spectroscopy is similar to atomic absorption spectrometry in that a sample absorbs light at a particular wavelength to promote its electrons from its ground electronic state into an excited state.
Spectroscopy in analytical chemistry is used in two primary manners: (1) to identify a species and (2) to quantify a species. Identification of a species involves recording the absorption or …
26/10/2011 · In this video Dr Warren Corns discusses Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy and the structure and operations of an Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometer. Category Science & Technology
Spectroscopy Problem Set What are bands observed for molecular spectra and lines for atomic spectra? 16. F = fluorescence; P = phosphorescence; E = excitation 17. In the diagram above the three labeled regions represent: _____ 17 18. Why is the phosphorescence lifetime longer than the one for fluorescence? 18 19. What are flicker, 60 Hz, and shot noises, how does appear in a power density
Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy analyzer for determination of mercury Fluorescence spectroscopy (also known as fluorimetry or spectrofluorometry ) is a type of electromagnetic spectroscopy that analyzes fluorescence from a sample.
Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry (AFS) is an ideal detection technique for speciation studies concerning hydride forming elements (mainly As, Se and Sb) and Hg. The analytical features of AFS,
Fluorescence Spectrophotometry Peter TC So,Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, spectroscopy. Instrumentation for Fluorescence Spectrophotometry The measurement of fluorescence signals provides a sensitive method of monitoring the biochemical environ-mentofafluorophore.Instrumentshavebeendesignedto measure fluorescence intensity, spectrum, …
2/15/16 9 ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY CH 8-10 CHEM 314 • DifferenBate between atomic and molecular spec. • Label, diagram, describe each of the following
Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, is intended for the rapid publication of both original work and reviews in the following fields: Atomic Emission (AES), Atomic Absorption (AAS) and Atomic Fluorescence (AFS) spectroscopy; Mass Spectrometry (MS) for inorganic
Atomic Emission Spectroscopy – Instrumental Chemistry – Lecture Slides, Slides for Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis. Ambedkar University, Delhi . Ambedkar University, Delhi. Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis, Biology and Chemistry. PDF (233 KB) 16 pages. 1000 Number of visits. Description. Main topics of the course are: Atomic Absorption, Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry, Atomic
2 ENVIRONMENT: WATER AND WASTE 0 1 (a) A F Resonance fluorescence 0 (b) 1 2 Direct line fluorescence A F 0 (c) 1 2 Stepwise line fluorescence A F Figure 1 Basic types of atomic …
Instrumentation for 2 Fluorescence Spectroscopy
Measurements of Absolute Atomic Nitrogen Density by Two
2 Instrumentation for Fluorescence Spectroscopy The successful application of fluorescence methods requires an understand ing of the instrumentation.
fluorescence spectroscopy (AFS) and x-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF). The latter is a The latter is a powerful analytical spectroscopic method, the technique utilises the x-rays by using them to
2 ENVIRONMENT: WATER AND WASTE 0 1 (a) A F Resonance fluorescence 0 (b) 1 2 Direct line fluorescence A F 0 (c) 1 2 Stepwise line fluorescence A F Figure 1 Basic types of atomic …
development of atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Surprisingly, detection limits Surprisingly, detection limits for the basic instruments used in flame atomic absorption and emission
This work describes the method of a selective hydride generation-cryotrapping (HG-CT) coupled to an extremely sensitive but simple in-house assembled and designed atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS) instrument for determination of toxicologically important As species.
• Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy – This method commonly uses a burner with a round burning outlet. The flame is used to solvate and atomize the sample, but a lamp
In its use as an analytical tool, this fluorescence radiation is the complement of the missing wavelengths in absorption spectroscopy. Thus, the emission lines will have a characteristic “fingerprint” that can be associated with a unique atom , ion, or molecule .
Instrumentation for Fluorescence Spectroscopy 27. monochromator. Similarly, the excitation spectrum would represent the relative emission of the fluorophore at each excitation wavelength. For most fluorophores the quantum yields and emission spectra are independent of excitation wavelength. As a result, the excitation spectrum of a fluo- rophore can be superimposable on its absorption …
Atomic absorption spectroscopy , Eg. AAS instrument ii. Atomic emission spectroscopy, ICP- OES iii. Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy, AFS Note: Atomization is usually achieved either by flames, electrically heating or by plasmas. Process Occurring in Flame (Gary D. Christian 6 th ed, pg 522) The solution is aspirated into the flame as a fine spray The solvent evaporates, leaving the dehydrated
The AF420 is a Simultaneous Double Beam Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometer provides elemental analysis for sub trace detection of hydride-forming elements.
Chemistry 311: Topic 2 – Atomic Spectroscopy A = log ≈ log P solvent P solution P 0 P t Beer’s Law: A = -log T = log P 0/P t = εbc ¾ However, this never realized as scattering and other losses also reduce
Click here to view our 2016 Products Catalog covering all our Analytical Instrumentation including X-ray Fluorescence(XRF) Spectrometry, Atomic Absorption Spectrometry, Chromatography, Mass Spectrometry and others.
(PDF) Measurements of Absolute Atomic Nitrogen Density by
Spectroscopy Problem Set February 22 2018
Spectroscopy in analytical chemistry is used in two primary manners: (1) to identify a species and (2) to quantify a species. Identification of a species involves recording the absorption or …
fluorescence spectroscopy (AFS) and x-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF). The latter is a The latter is a powerful analytical spectroscopic method, the technique utilises the x-rays by using them to
Atomic Absorption and Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy – Instrumental Chemistry – Lecture Slides, Slides for Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis.
Click here to view our 2016 Products Catalog covering all our Analytical Instrumentation including X-ray Fluorescence(XRF) Spectrometry, Atomic Absorption Spectrometry, Chromatography, Mass Spectrometry and others.
2 A typical atomic absorption instrument holds several lamps each for a different element. The lamps are housed in a rotating turret so that the correct
Flame Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy an overview
Instrumentation for 2 Fluorescence Spectroscopy
Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy uses the characteristic ways light interacts with the electronic structure of atoms to identify trace metals at very low concentrations.
A third field in atomic spectroscopy is atomic fluorescence. This technique incor – This technique incor – porates aspects of both atomic absorption and atomic emission.
Atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS) is a commonly employed method for elemental analysis employed with chemical vapor generation procedures due to its low cost and high sensitivity. Advances in AFS are reviewed for 2014 and 2015 involving instrumentation and …
• Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy – This method commonly uses a burner with a round burning outlet. The flame is used to solvate and atomize the sample, but a lamp
Click here to view our 2016 Products Catalog covering all our Analytical Instrumentation including X-ray Fluorescence(XRF) Spectrometry, Atomic Absorption Spectrometry, Chromatography, Mass Spectrometry and others.
introduction to fluorescence spectroscopy Download introduction to fluorescence spectroscopy or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get introduction to fluorescence spectroscopy …
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy Flame Atomic Emission Spectroscopy ICP Atomic Emission Spectroscopy. 1 BASIC PRINCIPLE ATOMIC ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY (AAS) is an analytical technique that measures the concentrations of elements. It makes use of the absorption of light by these elements in order to measure their concentration . – Atomic-absorption spectroscopy quantifies the …
Atomic Fluorescence. The process of excitation and decay to the ground state is involved in all three fields of atomic spectroscopy. Either the energy absorbed in the excitation process, or the energy emitted in the decay process is measured and used for analytical purposes.
Atomic Fluorescence Theory. The technique behind atomic fluorescence spectroscopy is similar to atomic absorption spectrometry in that a sample absorbs light at a particular wavelength to promote its electrons from its ground electronic state into an excited state.
Atomic Absorption and Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy – Instrumental Chemistry – Lecture Slides, Slides for Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis.
2 ENVIRONMENT: WATER AND WASTE 0 1 (a) A F Resonance fluorescence 0 (b) 1 2 Direct line fluorescence A F 0 (c) 1 2 Stepwise line fluorescence A F Figure 1 Basic types of atomic …
Fluorescence: Basic Instrumentation Of course laser sources have distinct emission lines characteristic of the atomic processes involved. The most commonly used lasers in modern biological fluorescence spectroscopy are the argon ion laser, the helium cadmium laser, the neodymium YAG (Nd:YAG) laser and, more recently, the titanium sapphire laser. The most commonly used argon ion …
Chemistry 311: Topic 2 – Atomic Spectroscopy A = log ≈ log P solvent P solution P 0 P t Beer’s Law: A = -log T = log P 0/P t = εbc ¾ However, this never realized as scattering and other losses also reduce
Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry (AFS) is an ideal detection technique for speciation studies concerning hydride forming elements (mainly As, Se and Sb) and Hg. The analytical features of AFS,
Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy Request PDF
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy 1st Edition – Elsevier
Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, is intended for the rapid publication of both original work and reviews in the following fields: Atomic Emission (AES), Atomic Absorption (AAS) and Atomic Fluorescence (AFS) spectroscopy; Mass Spectrometry (MS) for inorganic
This work describes the method of a selective hydride generation-cryotrapping (HG-CT) coupled to an extremely sensitive but simple in-house assembled and designed atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS) instrument for determination of toxicologically important As species.
instrument that uses this principle to analyze the concentration of metals in solution. The substances in a solution are suctioned into an excited phase where they undergo vaporization, and are broken down into small fragmented atoms by discharge, flame or plasma. Atomic Emission Spectroscopy • By exposing these atoms to such temperatures they are able to “jump” to high energy levels and
Atomic Absorption and Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy – Instrumental Chemistry – Lecture Slides, Slides for Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis.
Atomic Emission Spectroscopy – Instrumental Chemistry – Lecture Slides, Slides for Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis. Ambedkar University, Delhi . Ambedkar University, Delhi. Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis, Biology and Chemistry. PDF (233 KB) 16 pages. 1000 Number of visits. Description. Main topics of the course are: Atomic Absorption, Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry, Atomic
2 Instrumentation for Fluorescence Spectroscopy The successful application of fluorescence methods requires an understand ing of the instrumentation.
Spectroscopy in analytical chemistry is used in two primary manners: (1) to identify a species and (2) to quantify a species. Identification of a species involves recording the absorption or …
In its use as an analytical tool, this fluorescence radiation is the complement of the missing wavelengths in absorption spectroscopy. Thus, the emission lines will have a characteristic “fingerprint” that can be associated with a unique atom , ion, or molecule .
Atomic absorption spectroscopy , Eg. AAS instrument ii. Atomic emission spectroscopy, ICP- OES iii. Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy, AFS Note: Atomization is usually achieved either by flames, electrically heating or by plasmas. Process Occurring in Flame (Gary D. Christian 6 th ed, pg 522) The solution is aspirated into the flame as a fine spray The solvent evaporates, leaving the dehydrated
Flame Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy. Flame atomic absorption spectroscopy (FAAS) is suitable for measurement of a limited range of elements present at concentrations greater than approximately 1μgml−1 in biological fluids, and for the analysis of solutions obtained from biological tissues at the completion of the sample preparation steps.
graduate studies centered on the use of laser-excited atomic fluorescence spectroscopy for characterization of flames and plasmas used in analytical atomic spectrometry.
development of atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Surprisingly, detection limits Surprisingly, detection limits for the basic instruments used in flame atomic absorption and emission
Atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS) is a commonly employed method for elemental analysis employed with chemical vapor generation procedures due to its low cost and high sensitivity. Advances in AFS are reviewed for 2014 and 2015 involving instrumentation and …
2 A typical atomic absorption instrument holds several lamps each for a different element. The lamps are housed in a rotating turret so that the correct
Instrumentation for 2 Fluorescence Spectroscopy
ANALYSIS OF BISMUTH CONTENT IN A PEPTO-BISMOL TABLETS
Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy analyzer for determination of mercury Fluorescence spectroscopy (also known as fluorimetry or spectrofluorometry ) is a type of electromagnetic spectroscopy that analyzes fluorescence from a sample.
Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, is intended for the rapid publication of both original work and reviews in the following fields: Atomic Emission (AES), Atomic Absorption (AAS) and Atomic Fluorescence (AFS) spectroscopy; Mass Spectrometry (MS) for inorganic
In its use as an analytical tool, this fluorescence radiation is the complement of the missing wavelengths in absorption spectroscopy. Thus, the emission lines will have a characteristic “fingerprint” that can be associated with a unique atom , ion, or molecule .
2 Instrumentation for Fluorescence Spectroscopy The successful application of fluorescence methods requires an understand ing of the instrumentation.
26/10/2011 · In this video Dr Warren Corns discusses Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy and the structure and operations of an Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometer. Category Science & Technology
2 ENVIRONMENT: WATER AND WASTE 0 1 (a) A F Resonance fluorescence 0 (b) 1 2 Direct line fluorescence A F 0 (c) 1 2 Stepwise line fluorescence A F Figure 1 Basic types of atomic …
Instrumentation for Fluorescence Spectroscopy 27. monochromator. Similarly, the excitation spectrum would represent the relative emission of the fluorophore at each excitation wavelength. For most fluorophores the quantum yields and emission spectra are independent of excitation wavelength. As a result, the excitation spectrum of a fluo- rophore can be superimposable on its absorption …
Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy Mercury Detection
Measurements of Absolute Atomic Nitrogen Density by Two
26/10/2011 · In this video Dr Warren Corns discusses Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy and the structure and operations of an Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometer. Category Science & Technology
broad types: atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS), atomic emission spectroscopy (AES) and atomic fluorescence spectroscopy (AFS). These types differ in certain aspects of their fundamental principles, in the details of the instrumentation used and in the measurement details, for example, the limit of detection. In all cases, however, the spectroscopic absorption, emission and fluorescence
laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy (LIF) that generally allows d irect access to the density of the non – emissive species a s atomic ground state s and also metastables.
Flame Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy. Flame atomic absorption spectroscopy (FAAS) is suitable for measurement of a limited range of elements present at concentrations greater than approximately 1μgml−1 in biological fluids, and for the analysis of solutions obtained from biological tissues at the completion of the sample preparation steps.
2 A typical atomic absorption instrument holds several lamps each for a different element. The lamps are housed in a rotating turret so that the correct
Atomic Absorption and Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy – Instrumental Chemistry – Lecture Slides, Slides for Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis.
laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy (LIF) that generally allows direct access to the density of the non-emissive species as atomic ground states and also metastables.
instrument that uses this principle to analyze the concentration of metals in solution. The substances in a solution are suctioned into an excited phase where they undergo vaporization, and are broken down into small fragmented atoms by discharge, flame or plasma. Atomic Emission Spectroscopy • By exposing these atoms to such temperatures they are able to “jump” to high energy levels and
graduate studies centered on the use of laser-excited atomic fluorescence spectroscopy for characterization of flames and plasmas used in analytical atomic spectrometry.
Atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS) is a commonly employed method for elemental analysis employed with chemical vapor generation procedures due to its low cost and high sensitivity. Advances in AFS are reviewed for 2014 and 2015 involving instrumentation and …
introduction to fluorescence spectroscopy Download introduction to fluorescence spectroscopy or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get introduction to fluorescence spectroscopy …
The AF420 is a Simultaneous Double Beam Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometer provides elemental analysis for sub trace detection of hydride-forming elements.
Spectroscopy in analytical chemistry is used in two primary manners: (1) to identify a species and (2) to quantify a species. Identification of a species involves recording the absorption or …
Strategic Information for the Life Science and Analytical Instrument Industry
Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy IBO
Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry a suitable detection
2/15/16 9 ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY CH 8-10 CHEM 314 • DifferenBate between atomic and molecular spec. • Label, diagram, describe each of the following
In its use as an analytical tool, this fluorescence radiation is the complement of the missing wavelengths in absorption spectroscopy. Thus, the emission lines will have a characteristic “fingerprint” that can be associated with a unique atom , ion, or molecule .
Atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS) is a commonly employed method for elemental analysis employed with chemical vapor generation procedures due to its low cost and high sensitivity. Advances in AFS are reviewed for 2014 and 2015 involving instrumentation and …
Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy analyzer for determination of mercury Fluorescence spectroscopy (also known as fluorimetry or spectrofluorometry ) is a type of electromagnetic spectroscopy that analyzes fluorescence from a sample.
introduction to fluorescence spectroscopy Download introduction to fluorescence spectroscopy or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get introduction to fluorescence spectroscopy …
Atomic Emission Spectroscopy – Instrumental Chemistry – Lecture Slides, Slides for Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis. Ambedkar University, Delhi . Ambedkar University, Delhi. Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis, Biology and Chemistry. PDF (233 KB) 16 pages. 1000 Number of visits. Description. Main topics of the course are: Atomic Absorption, Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry, Atomic
Atomic Fluorescence Theory. The technique behind atomic fluorescence spectroscopy is similar to atomic absorption spectrometry in that a sample absorbs light at a particular wavelength to promote its electrons from its ground electronic state into an excited state.
Figure 1. Arizona Instrument’s J505 Atomic Fluorescence Analyzer. Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy (AFS) In AFS, the excitation of an atom by an input of energy causes one of its electrons to move from a stable ground state to a higher energy, unstable excited state.
Flame Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy. Flame atomic absorption spectroscopy (FAAS) is suitable for measurement of a limited range of elements present at concentrations greater than approximately 1μgml−1 in biological fluids, and for the analysis of solutions obtained from biological tissues at the completion of the sample preparation steps.
Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry (AFS) is an ideal detection technique for speciation studies concerning hydride forming elements (mainly As, Se and Sb) and Hg. The analytical features of AFS,
Atomic Spectroscopy Andor Learning Centre
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy 1st Edition – Elsevier
The AF420 is a Simultaneous Double Beam Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometer provides elemental analysis for sub trace detection of hydride-forming elements.
• Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy – This method commonly uses a burner with a round burning outlet. The flame is used to solvate and atomize the sample, but a lamp
Spectroscopy Problem Set What are bands observed for molecular spectra and lines for atomic spectra? 16. F = fluorescence; P = phosphorescence; E = excitation 17. In the diagram above the three labeled regions represent: _____ 17 18. Why is the phosphorescence lifetime longer than the one for fluorescence? 18 19. What are flicker, 60 Hz, and shot noises, how does appear in a power density
introduction to fluorescence spectroscopy Download introduction to fluorescence spectroscopy or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get introduction to fluorescence spectroscopy …
Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry (AFS) is an ideal detection technique for speciation studies concerning hydride forming elements (mainly As, Se and Sb) and Hg. The analytical features of AFS,
2 Instrumentation for Fluorescence Spectroscopy The successful application of fluorescence methods requires an understand ing of the instrumentation.
Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy (AFS) is a very sensitive and selective method for the determination of a number of environmentally and biomedically important elements such as …
Flame Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy. Flame atomic absorption spectroscopy (FAAS) is suitable for measurement of a limited range of elements present at concentrations greater than approximately 1μgml−1 in biological fluids, and for the analysis of solutions obtained from biological tissues at the completion of the sample preparation steps.
instrument that uses this principle to analyze the concentration of metals in solution. The substances in a solution are suctioned into an excited phase where they undergo vaporization, and are broken down into small fragmented atoms by discharge, flame or plasma. Atomic Emission Spectroscopy • By exposing these atoms to such temperatures they are able to “jump” to high energy levels and
A third field in atomic spectroscopy is atomic fluorescence. This technique incor – This technique incor – porates aspects of both atomic absorption and atomic emission.
Luminescence and the nature of light A hot body that emits radiation solely because of its high temperature is said to exhibit incan-descence. All other forms of light emission are
Instrumentation for Fluorescence Spectroscopy 27. monochromator. Similarly, the excitation spectrum would represent the relative emission of the fluorophore at each excitation wavelength. For most fluorophores the quantum yields and emission spectra are independent of excitation wavelength. As a result, the excitation spectrum of a fluo- rophore can be superimposable on its absorption …
2 ENVIRONMENT: WATER AND WASTE 0 1 (a) A F Resonance fluorescence 0 (b) 1 2 Direct line fluorescence A F 0 (c) 1 2 Stepwise line fluorescence A F Figure 1 Basic types of atomic …
Atomic spectroscopy • atomic spectroscopy refers to measurement of elemental concentrations via optical processes of absorption, emission or fluorescence as
Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy IBO
Fundamentals AAS e 07-05-29 Lab Instruments Suppliers
In its use as an analytical tool, this fluorescence radiation is the complement of the missing wavelengths in absorption spectroscopy. Thus, the emission lines will have a characteristic “fingerprint” that can be associated with a unique atom , ion, or molecule .
laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy (LIF) that generally allows d irect access to the density of the non – emissive species a s atomic ground state s and also metastables.
laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy (LIF) that generally allows direct access to the density of the non-emissive species as atomic ground states and also metastables.
Instrumentation for Fluorescence Spectroscopy 27. monochromator. Similarly, the excitation spectrum would represent the relative emission of the fluorophore at each excitation wavelength. For most fluorophores the quantum yields and emission spectra are independent of excitation wavelength. As a result, the excitation spectrum of a fluo- rophore can be superimposable on its absorption …
Atomic Fluorescence. The process of excitation and decay to the ground state is involved in all three fields of atomic spectroscopy. Either the energy absorbed in the excitation process, or the energy emitted in the decay process is measured and used for analytical purposes.
Atomic Fluorescence Theory. The technique behind atomic fluorescence spectroscopy is similar to atomic absorption spectrometry in that a sample absorbs light at a particular wavelength to promote its electrons from its ground electronic state into an excited state.
Spectroscopy Problem Set What are bands observed for molecular spectra and lines for atomic spectra? 16. F = fluorescence; P = phosphorescence; E = excitation 17. In the diagram above the three labeled regions represent: _____ 17 18. Why is the phosphorescence lifetime longer than the one for fluorescence? 18 19. What are flicker, 60 Hz, and shot noises, how does appear in a power density
Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy analyzer for determination of mercury Fluorescence spectroscopy (also known as fluorimetry or spectrofluorometry ) is a type of electromagnetic spectroscopy that analyzes fluorescence from a sample.
2 A typical atomic absorption instrument holds several lamps each for a different element. The lamps are housed in a rotating turret so that the correct
Fluorescence: Basic Instrumentation Of course laser sources have distinct emission lines characteristic of the atomic processes involved. The most commonly used lasers in modern biological fluorescence spectroscopy are the argon ion laser, the helium cadmium laser, the neodymium YAG (Nd:YAG) laser and, more recently, the titanium sapphire laser. The most commonly used argon ion …
2 ENVIRONMENT: WATER AND WASTE 0 1 (a) A F Resonance fluorescence 0 (b) 1 2 Direct line fluorescence A F 0 (c) 1 2 Stepwise line fluorescence A F Figure 1 Basic types of atomic …
Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy uses the characteristic ways light interacts with the electronic structure of atoms to identify trace metals at very low concentrations.
Atomic Emission Spectroscopy PDF documents
Speciation Analysis of Arsenic by Selective Hydride
Figure 1. Arizona Instrument’s J505 Atomic Fluorescence Analyzer. Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy (AFS) In AFS, the excitation of an atom by an input of energy causes one of its electrons to move from a stable ground state to a higher energy, unstable excited state.
Atomic Emission Spectroscopy – Instrumental Chemistry – Lecture Slides, Slides for Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis. Ambedkar University, Delhi . Ambedkar University, Delhi. Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis, Biology and Chemistry. PDF (233 KB) 16 pages. 1000 Number of visits. Description. Main topics of the course are: Atomic Absorption, Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry, Atomic
Spectroscopy in analytical chemistry is used in two primary manners: (1) to identify a species and (2) to quantify a species. Identification of a species involves recording the absorption or …
Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, is intended for the rapid publication of both original work and reviews in the following fields: Atomic Emission (AES), Atomic Absorption (AAS) and Atomic Fluorescence (AFS) spectroscopy; Mass Spectrometry (MS) for inorganic
Click here to view our 2016 Products Catalog covering all our Analytical Instrumentation including X-ray Fluorescence(XRF) Spectrometry, Atomic Absorption Spectrometry, Chromatography, Mass Spectrometry and others.
• Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy – This method commonly uses a burner with a round burning outlet. The flame is used to solvate and atomize the sample, but a lamp
Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy uses the characteristic ways light interacts with the electronic structure of atoms to identify trace metals at very low concentrations.
instrument that uses this principle to analyze the concentration of metals in solution. The substances in a solution are suctioned into an excited phase where they undergo vaporization, and are broken down into small fragmented atoms by discharge, flame or plasma. Atomic Emission Spectroscopy • By exposing these atoms to such temperatures they are able to “jump” to high energy levels and
ANALYSIS OF BISMUTH CONTENT IN A PEPTO-BISMOL TABLETS
Atomic Spectroscopy Andor Learning Centre
Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy (AFS) is a very sensitive and selective method for the determination of a number of environmentally and biomedically important elements such as …
Spectroscopy Problem Set What are bands observed for molecular spectra and lines for atomic spectra? 16. F = fluorescence; P = phosphorescence; E = excitation 17. In the diagram above the three labeled regions represent: _____ 17 18. Why is the phosphorescence lifetime longer than the one for fluorescence? 18 19. What are flicker, 60 Hz, and shot noises, how does appear in a power density
Fluorescence Spectrophotometry Peter TC So,Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, spectroscopy. Instrumentation for Fluorescence Spectrophotometry The measurement of fluorescence signals provides a sensitive method of monitoring the biochemical environ-mentofafluorophore.Instrumentshavebeendesignedto measure fluorescence intensity, spectrum, …
development of atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Surprisingly, detection limits Surprisingly, detection limits for the basic instruments used in flame atomic absorption and emission
Atomic Absorption and Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy – Instrumental Chemistry – Lecture Slides, Slides for Chemical Instrumentation and Analysis.
Atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS) is a commonly employed method for elemental analysis employed with chemical vapor generation procedures due to its low cost and high sensitivity. Advances in AFS are reviewed for 2014 and 2015 involving instrumentation and …
instrument that uses this principle to analyze the concentration of metals in solution. The substances in a solution are suctioned into an excited phase where they undergo vaporization, and are broken down into small fragmented atoms by discharge, flame or plasma. Atomic Emission Spectroscopy • By exposing these atoms to such temperatures they are able to “jump” to high energy levels and
Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy uses the characteristic ways light interacts with the electronic structure of atoms to identify trace metals at very low concentrations.
2 ENVIRONMENT: WATER AND WASTE 0 1 (a) A F Resonance fluorescence 0 (b) 1 2 Direct line fluorescence A F 0 (c) 1 2 Stepwise line fluorescence A F Figure 1 Basic types of atomic …
fluorescence spectroscopy (AFS) and x-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF). The latter is a The latter is a powerful analytical spectroscopic method, the technique utilises the x-rays by using them to
This work describes the method of a selective hydride generation-cryotrapping (HG-CT) coupled to an extremely sensitive but simple in-house assembled and designed atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS) instrument for determination of toxicologically important As species.
Spectroscopy in analytical chemistry is used in two primary manners: (1) to identify a species and (2) to quantify a species. Identification of a species involves recording the absorption or …
Fluorescence: Basic Instrumentation Of course laser sources have distinct emission lines characteristic of the atomic processes involved. The most commonly used lasers in modern biological fluorescence spectroscopy are the argon ion laser, the helium cadmium laser, the neodymium YAG (Nd:YAG) laser and, more recently, the titanium sapphire laser. The most commonly used argon ion …
2/15/16 9 ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY CH 8-10 CHEM 314 • DifferenBate between atomic and molecular spec. • Label, diagram, describe each of the following
A third field in atomic spectroscopy is atomic fluorescence. sorption. The ease and speed at which precise and accurate determinations can be made with this technique have made atomic ab- sorption one of the most popular methods for the determination of metals. Aspirating a solution of the sample into a flame aligned in the light beam serves this purpose. The capability of an atom to absorb
Atomic Fluorescence. The process of excitation and decay to the ground state is involved in all three fields of atomic spectroscopy. Either the energy absorbed in the excitation process, or the energy emitted in the decay process is measured and used for analytical purposes.
Atomic Absorption & Fluorescence Spectroscopy G.F
Fluorescence Spectrophotometry Peter TC So,Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, spectroscopy. Instrumentation for Fluorescence Spectrophotometry The measurement of fluorescence signals provides a sensitive method of monitoring the biochemical environ-mentofafluorophore.Instrumentshavebeendesignedto measure fluorescence intensity, spectrum, …
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy 1st Edition – Elsevier
Speciation Analysis of Arsenic by Selective Hydride
Measurements of Absolute Atomic Nitrogen Density by Two
2 A typical atomic absorption instrument holds several lamps each for a different element. The lamps are housed in a rotating turret so that the correct
ANALYSIS OF BISMUTH CONTENT IN A PEPTO-BISMOL TABLETS
Mercury Vapor Analysis Using Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy
Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy Mercury Detection